Next to aviation, motorsport is the fastest-developing direction in the world. Less than two centuries have passed since the invention of the first gasoline-powered cars. However, man’s desire to find out how fast these could go gave birth to the sport of auto racing, starting the chain of famous motoring disciplines worldwide, such as the IndyCar–1909, the Rally Monte Carlo–1911, and even the 24 Hours of Le Mans–1923. The modernization process was progressive and fascinating. How, in less than 150 years, we’ve gone from the very first race car and road racing to today’s high-tech hybrid vehicles and motorsport?
- Who Invented The Car First: Carl Benz Or Gottlieb Daimler?
- First Attempts At Car Racing
- The Birth Of Competitive Racing
- The Godfathers of Power and Speed
- The Breakthroughs of Motorsport's development
- The Global Racing Revolution
- Who Were The Female Pioneers In The Motorsport?
- The Shift to Hybrid Technologies (1990s-Present)
- Takeaways
Who Invented The Car First: Carl Benz Or Gottlieb Daimler?
Carl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler were the forefathers of automobile racing, simultaneously creating the world’s first gasoline-powered vehicles.
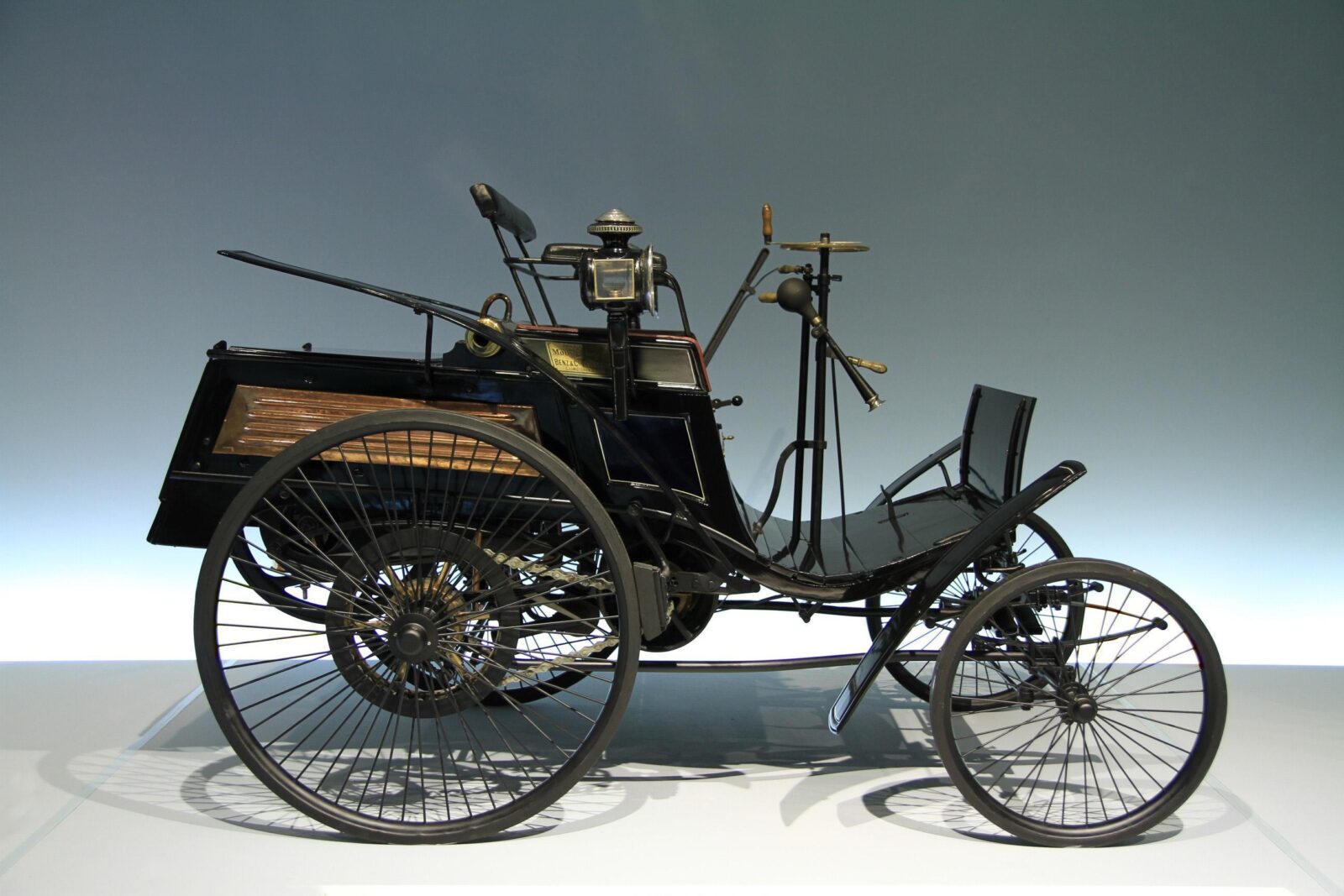
After the first stationary gasoline engine, which brought Carl Benz commercial success in 1879, he designed a three-wheeled Benz Motor Car model no. 1, the Motorwagen, with its engine in 1885 – the world’s first car.
On the other hand, Gottlieb Daimler, the first to use a gasoline engine in a two-wheeled vehicle, developed the forerunner of the modern automobile engine in the same -1885.
Daimler centered on repeating success with the four-wheeled car. With the help of Wilhelm Maybach, he adapted it to a stagecoach and designed the world’s first four-wheeled automobile in 1886.
Carl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler had never met personally and worked at different places: Mannheim and Stuttgart. However, Benz became the first to invent the car because he received the patent first in 1886.
With getting the milestone, a question arose: whose vehicle was superior? The answer, it seemed, could only be determined by pitting those three and four-wheeled cars against each other in a race.
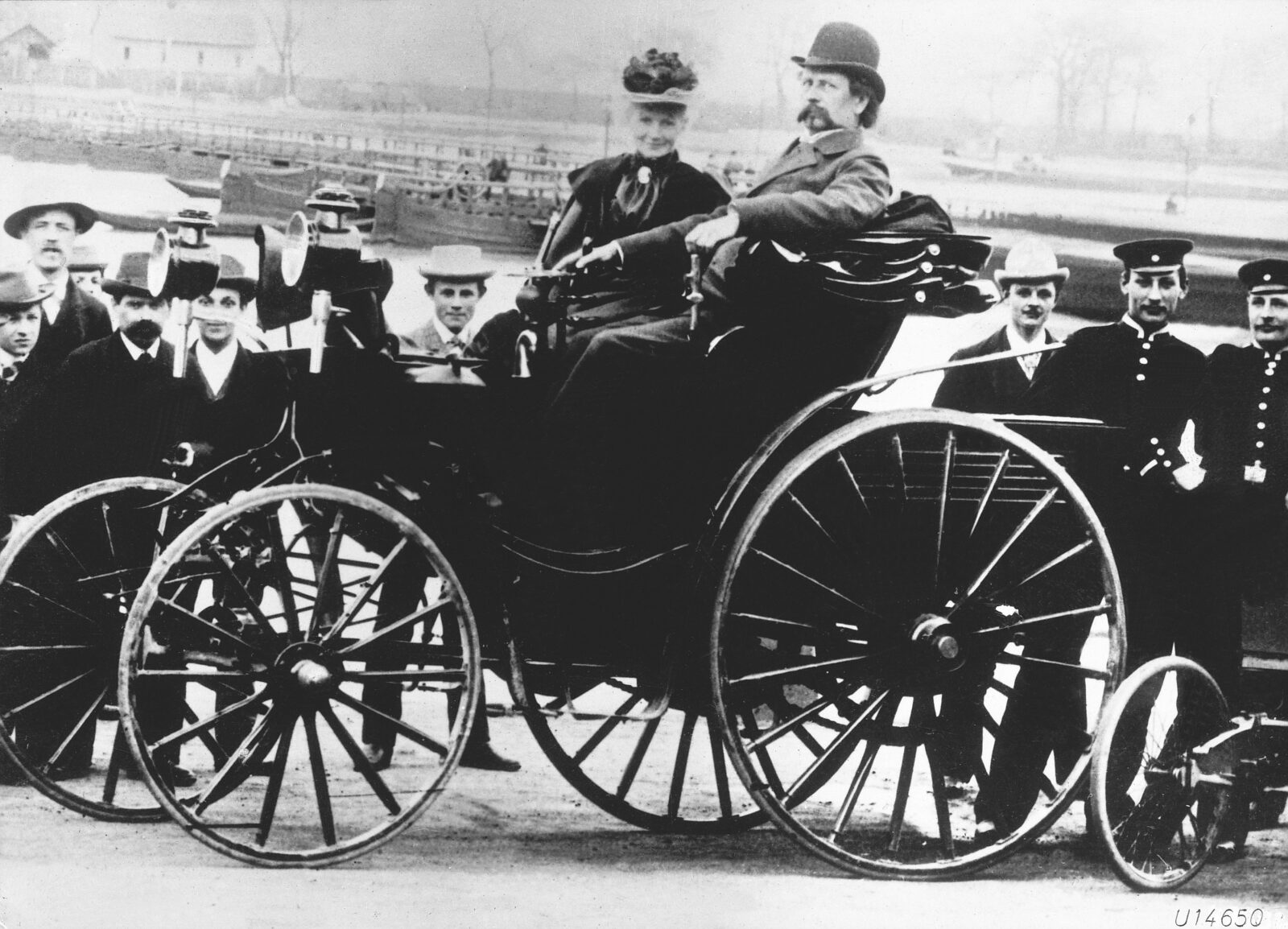

First Attempts At Car Racing
Did you know that motorsports got its ‘elite sport’ label from its origins? Because at a time when most citizens rode horses, only the rich could afford gasoline cars. Therefore, automobiles were a lot of wealthy entrepreneurs.
All the early competitions were closed challenges, where each wished to claim their car as the best to sell more.
So there were no requirements and no rules, but there were many start-up entrepreneurs, talented engineers, and car enthusiasts, while newspapers became the major car advertisers and race promoters.
Bois de Boulogne (France 1887)
Organized by the editor-in-chief of Le Vélocipède, Monsieur Fossier, the first attempt at a car race was far from the challenge we are used to, as there was one driver who won the event appropriately.
Jules-Albert de Dion founded De Dion-Bouton – the world’s largest automobile manufacturer, and together with George Bouton, they designed a steam-powered vehicle, in which Bouton ran a 2km race from the Pont de Neuilly to the Bois de Boulogne on 28 April 1887.
Paris-Rouen (France 1894)
The Paris-Rouen on 22 July 1894 was the second attempt to hold a car race. The chief editor of Le Petit Journal, Pierre Giffard, announced the ‘Competition for Horseless Carriages’ with the top prize of 5,000 francs going to ‘the competitor whose car comes closest to the ideal.’
And that was a bit closer to the traditional competition, even though the event suited a rally format. 25 of the 69 cars from serious manufacturers like Peugeot, Panhard, and De Dion to amateur owners started the race. One after the other, the drivers set off in an order separated by 30 seconds.
On the board, each driver had a judge, who was responsible for the crew maintaining the rules and evaluating with a score of 0 to 20, based on how easy the vehicle was to drive, its simple design, and aesthetics.
With a steam engine designed by Gottlieb Daimler, Count Jules-Albert de Dion took first, traveling at an average speed of 19 km/h. He finished ahead of Albert Lemaître (Peugeot), Auguste Doriot (Peugeot), René Panhard (Panhard), and Émile Levassor (Panhard). But Jules-Albert de Dion didn’t win because his car didn’t score enough, so Peugeot and Panhard-Levassor shared victory.
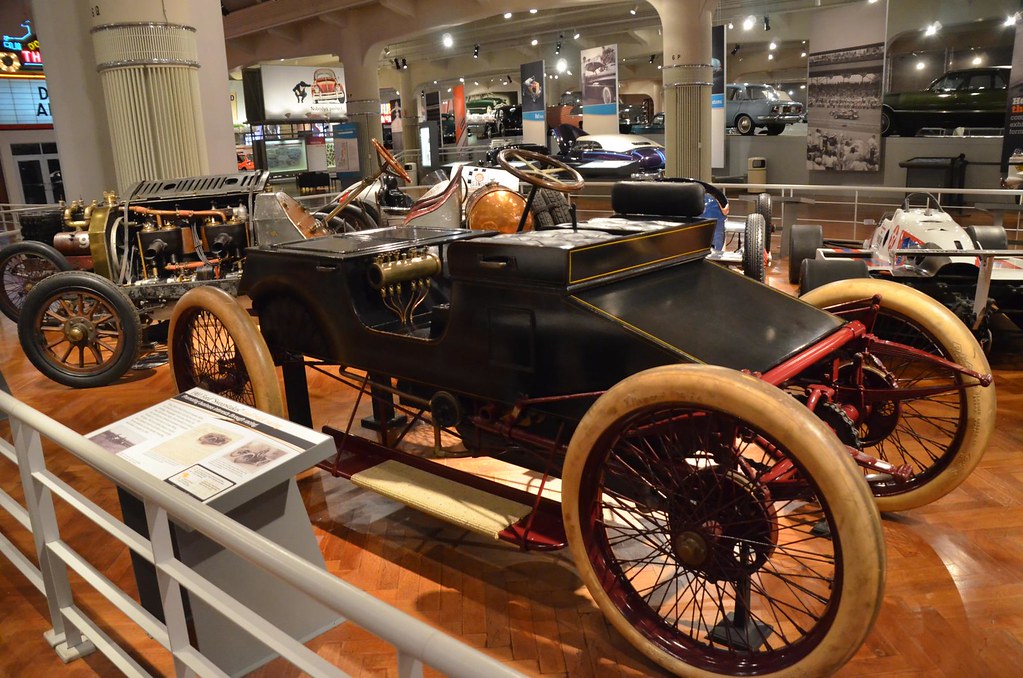

The Birth Of Competitive Racing
Paris–Bordeaux–Paris (France 1895)
However, the following Bordeaux-Paris race in 1895 finally became the first motor racing challenge because the event got its competitive look.
Built specifically for racing, the Panhard-Levassor 1205cc model, with a twin-cylinder engine running at 750 rpm, completed 1,178 km first. Alone, Émile Levassor had raced for about 49 hours and finished six hours ahead of the competitors.
On the Paris-Bordeaux-Paris route, Levassor met the passionate racing driver Baron René de Knyff, who had recently led the Commission Sportive Internationale (CSI), better known as the FIA, which was founded in 1904, from 1922 to 1946.
However, Émile Levassor was disqualified because his 1205cc was a two-seater car instead of a four, as it required.
Peugeot, equipped with the Daimler engine, became the official winner of Paris-Rouen, launching the era of Mercedes-Benz. In 1926, they joined with Carl Benz to form Daimler-Benz, now known as the Mercedes-Benz Group.
However, Émile Levassor and René Panhard played a role in the Car Club de France’s foundation. They established France as the birthplace of motor racing and the country as the leading nation in the automotive industry.
In the same 1895 year, an American business and publisher, Herman Henry Kohlsaat, organized the USA’s first motor race – Chicago Times-Herald, which marked the beginning of a long history of motor racing in the United States. Racing against five participants, Frank Duryea won the challenge.
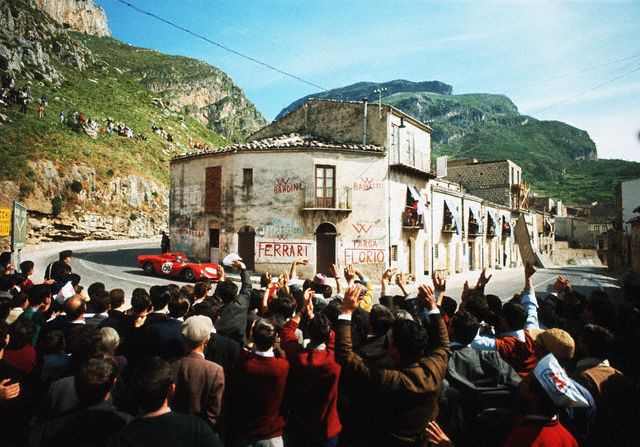

Targa Florio (Italy 1906)
After the Paris-Rouen, Targa Florio set the foundation for future endurance races, influencing the format and structure of events like the Mille Miglia and the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
After winning the Coppa Florio, car enthusiast Vincenzo Florio organized his race – the Targa Florio – in 1906. The event caught the world’s attention, with the famous artist designing medals and magazines publishing graphic reproductions of the race, cars, and speeds.
Imagine the Targa Florio race, which starts on public roads in the Sicilian mountains, three laps of a 148 km circuit, totaling 444 km through challenging terrain, sharp turns, steep climbs, and narrow sidewalks, testing the skill of the driver and the endurance of the vehicle.
The Targa Florio pushed the boundaries of automotive technology because durability and reliability were emphasized over sheer speed, while manufacturers sought to create vehicles that could withstand the rigors of such demanding courses.
The event has been reborn as a regular race for classic and vintage cars. However, to be held until 1977, Targa Florio saw many legendary drivers, including Tazio Nuvolari, Stirling Moss, and Juan Manuel Fangio, cementing its status as a prestigious event and forming ground for future racing challenges. At the time, the future Red Bull advisor Helmut Marko called the circuit ‘totally insane.‘
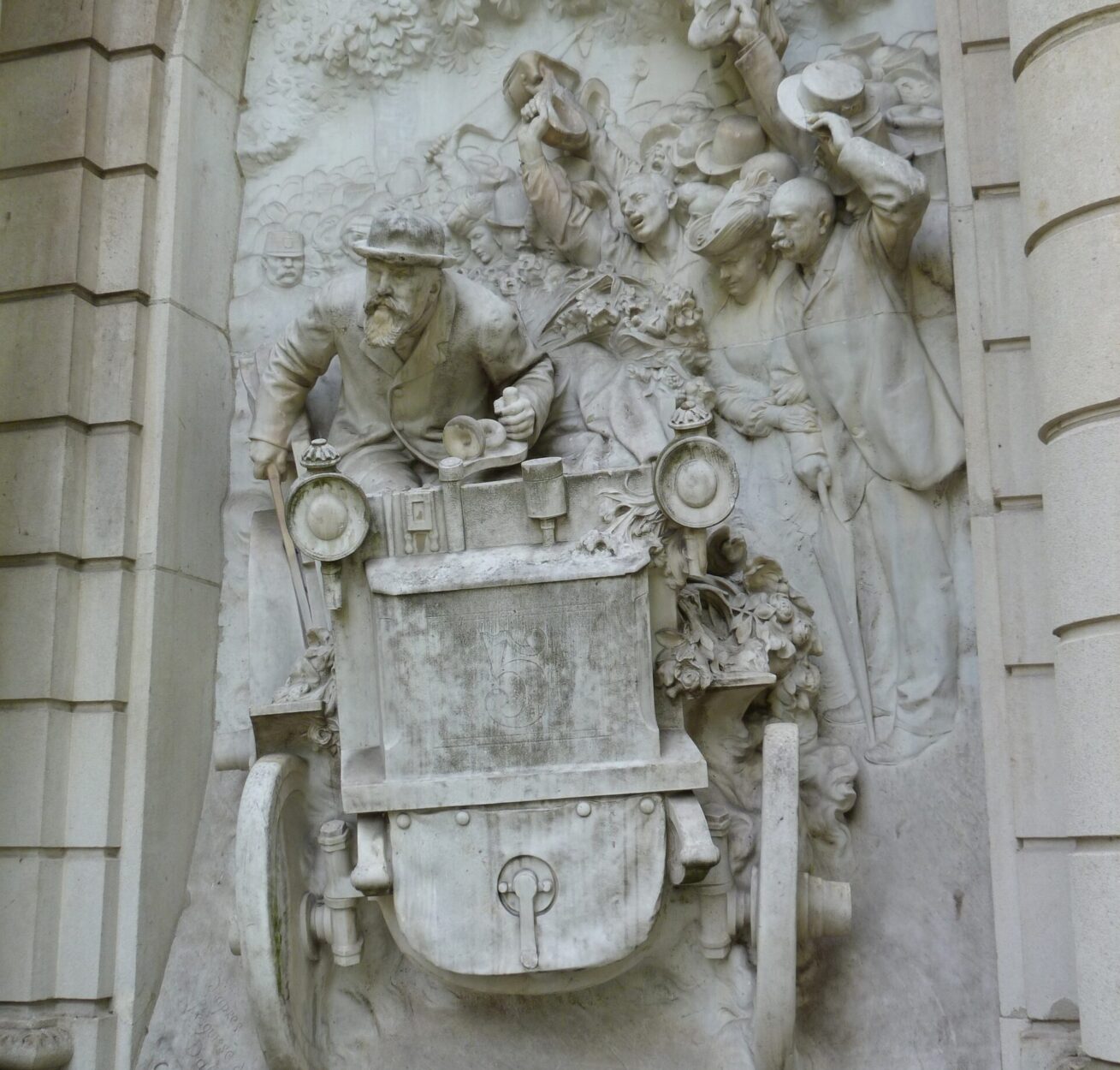

The Godfathers of Power and Speed
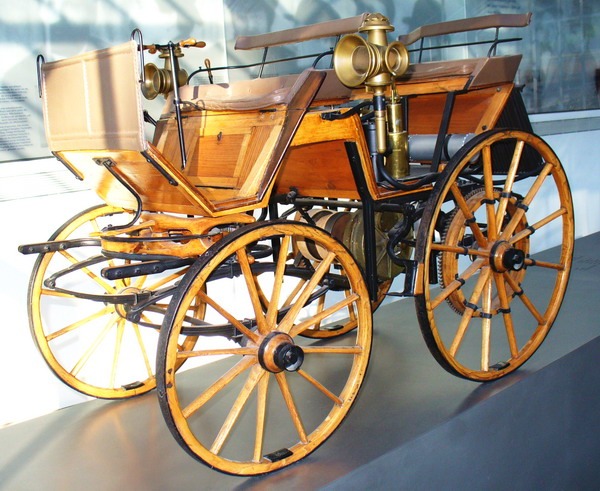
Émile Levassor and René Panhard had supplied Daimler-upgraded vehicles under the Panhard et Levassor since 1887. In 1891, Émile Levassor offered a significantly superior car specifically designed for racing. Thus, the Panhard et Levassor P2C (Type A) became the world’s first race car because the vehicle had a front-mounted engine and innovative transmission system.
Émile Levassor also played a significant role in the development of Peugeot. Founded in 1810 by Armand Peugeot, the manufactury produced bicycles and then three-wheeled, steam-powered cars. However, after Armand Peugeot met Émile Levassor in 1890, he became enthusiastic about a four-wheeled, gasoline-powered carriage built by Panhard under license from Daimler. Peugeot also became the first manufacturer to put rubber tires on a petrol-powered car.
Moreover, Émile Levassor and René Panhard came first with the concept of racing press coverage. Both sought to raise the public to stick with their cars. However, they weren’t the only ones, as the process had leaped forward with giant strides.
In 1894, Carl Benz revealed the Benz Velo – a car designed specifically for racing. Powered by a single-cylinder engine, producing 3hp, Velo had a top speed of about 30 km/h.
In the United Kingdom, the ‘Big Three‘ English car engineers set car racing to quite another level.
Thus, exploring the engines, Frederick W. Lanchester invented the first British-made racing car in 1895. Lanchester was the first to design an epicyclic gearbox before Henry Ford adopted it and the first to use a caliper-type automotive disc brake, which he patented in 1902.
Harry Ricardo was known for his work on the design of the combustion chamber and the development of the ‘Ricardo Combustion Chamber‘.
Finally, in partnership with Charles Rolls, another British engineer, Henry Royce, introduced the Rolls-Royce 10hp in 1904, and his marque was renowned for having the most reliable, powerful, and efficient engine.
In the United States, brothers engineers Frank and Charles Duryea designed the first American-made car in 1893 and founded the Duryea Motor Wagon Company in 1895, which cars became the first automobiles sold in the United States.
Mercedes unveiled a powerful race-dominated 35 HP car in 1901, even though Henry Ford truly grasped the potential of racing to promote his brand. Although he founded Ford Motor Company in 1903, his Sweepstakes car, built with winnings from a race against Alexander Winton in 1901, established Ford as a force to be reckoned with.
Brothers Giovanni, Ernesto Agnelli, and Matteo Ceirano formed the Italian automotive industry. In 1899, Giovanni Agnelli founded the Fabbrica Italiana di Automobili Torino, better known as FIAT, and designed their first 4 HP car in the same year.
Along with new manufacturers, designers, and cars, that time saw its racing legends, and Barney Oldfield was that one. His name was the synonym for speed because he had participated in 49 races over ten years! Moreover, he was the first to drive a car at 96 km/h.

The Breakthroughs of Motorsport’s development
Nothing could stop motorsport from rising since the Bordeaux-Paris and Chicago Times-Herald races as the world had been changing to petrol automobiles, while races became the significant challenges that determined the best cars.
Automobile Clubs and International Rising
United by their passion for motor racing, all the participants in the Bordeaux-Paris race were so happy to meet each other that they thought it would be an unforgivable mistake to lose their connection, hence the birth of the Automobile Club de France (ACF).
In 1899, the ACF held the first-ever Tour de France Automobile race. Guess who won the race? It was René de Knyff at the wheel of Panhard et Levassor’s car.
With the offer of the ACF, an American millionaire and owner of the New York Herald, James Gordon Bennett Jr., organized the prestigious Gordon Bennett Cup in 1900. It was the first international race, which gathered the national automobile clubs of Great Britain, the United States, Germany, France, Austria, Belgium, Italy, and Switzerland.
The annual event was held until 1905, when the French Automobile Club switched to the French Grand Prix on June 26 and 27, 1906, near Le Mans. By this time, the ‘Grand Prix’ label already existed, as the Automobile Club du Béarn had organized the Pau Grand Prix in 1901.
In 1908, the United States of America became the first country outside France to host an automobile race using the name Grand Prix (Grand Prize), even though it was a strictly local affair, far from international fame.
With the support of the ACF, the Spanish Automobile Club organized the Paris–Madrid race in May 1903, where René de Knyff and Charles S. Rolls were racing with Panhard-Levassor, which already could reach 130 km/h!
In 1904, William Kissam Vanderbilt II created the Vanderbilt Cup in New York, the first major trophy in American motorsport.

First Racing Circuits And The People Behind Them
Motorsport’s formation was a global process, and soon purpose-built racetracks such as Brooklands in the United Kingdom (1907), Indianapolis Motor Speedway in the United States (1909), and Monza Circuit in Italy (1922) were constructed, even though the Australian Aspendale Racecourse in 1906, was the first.
Aspendale Racecourse (1906)
Aspendale Park Racecourse was designed as a horse track and was named in honor of owner James Robert Crooke’s favorite horse, Aspen.
However, motor racing was Crooke’s second passion, so in 1905, he built the first commercial racetrack within the existing horse track and held its first race meeting in January 1906. The track ceased operations before World War II.
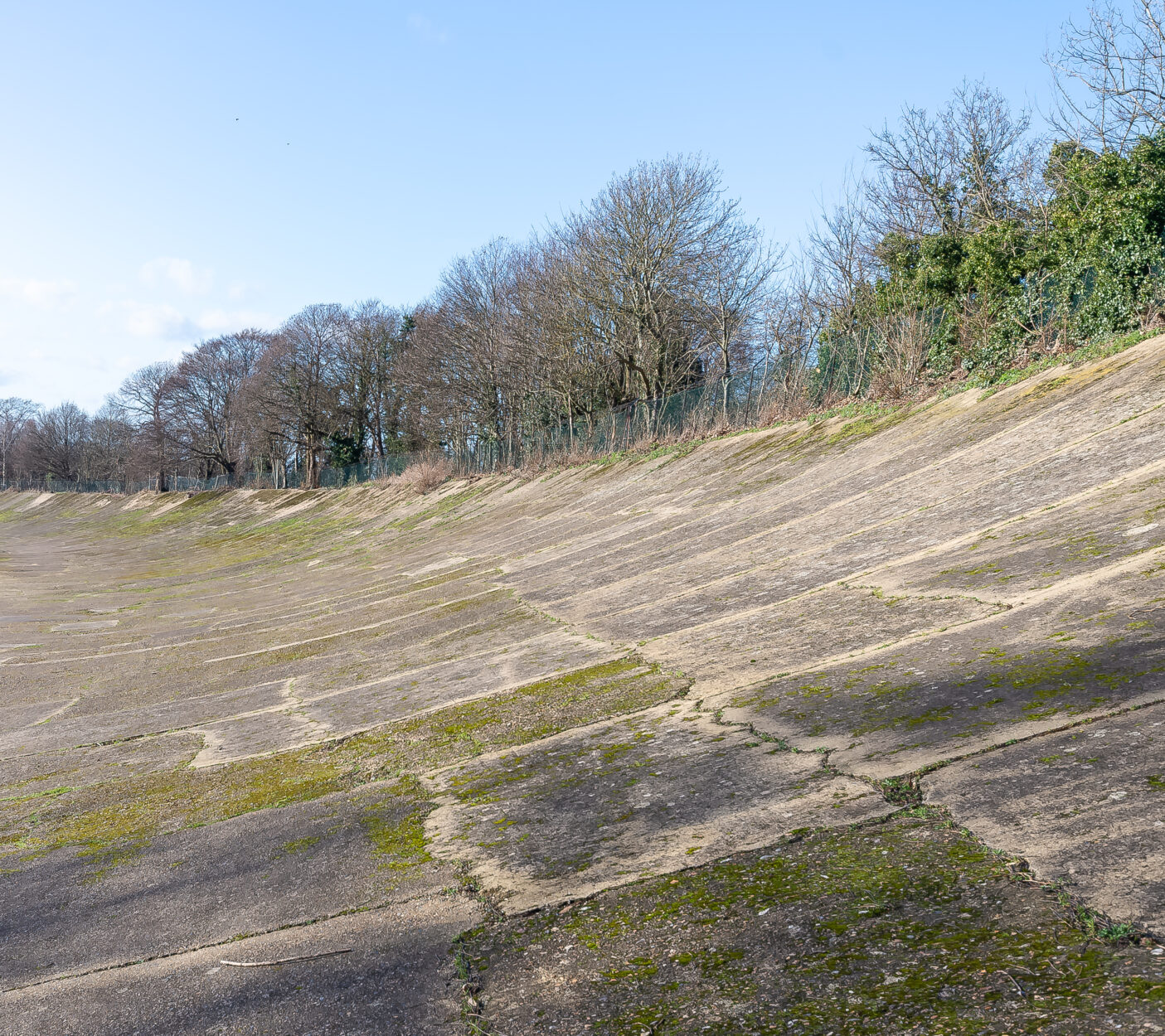

Brooklands (1907)
The first ever banked oval, a 4.453 km motor racing circuit in the United Kingdom, was once one of Britain’s largest airfields.
Hugh Fortescue Locke-King founded Brooklands around his estate in 1906 to improve the British car industry, as over 50% of the market was French cars. They needed a perfect race track, and Brooklands fit the bill. The first race was held in 1907 and attracted some of Britain’s most famous names, including Charles Rolls.
The Fifty-Foot Line is a notable feature of the track. A dotted black line down the middle of the track was thought to be the trajectory on which the racer could take the banked corners without using the steering wheel.
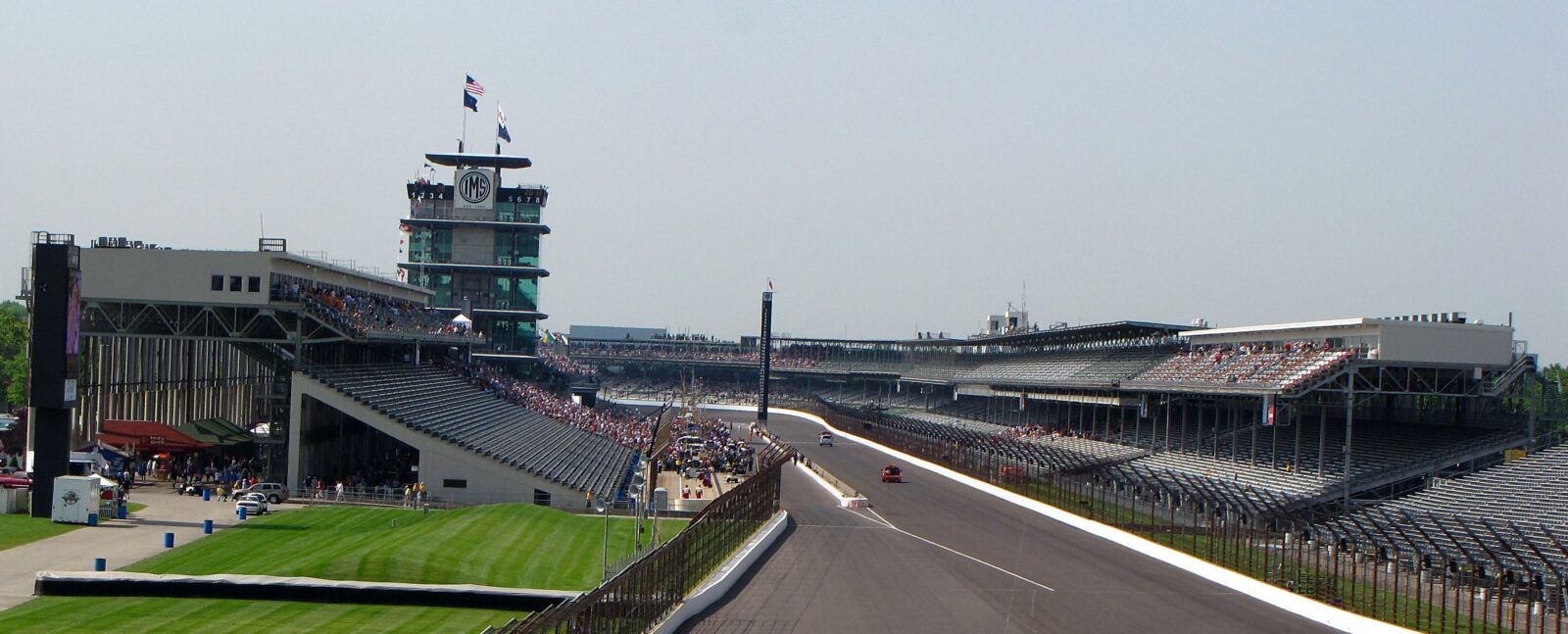

Indianapolis Motor Speedway (1909)
Without exaggeration, Indianapolis Motor Speedway (IMS) is the most legendary race track in the United States.
The man behind the idea and father of the Indy 500, Carl G. Fisher, was always in a hurry to do something big. After witnessing the motoring frenzy in France and visiting Brooklands, Fisher wanted to build the world’s greatest racetrack in the United States, where manufacturers could test cars at sustained speeds while drivers learned their limits.
Under the Federation of American Motorcyclists (FAM), the Indianapolis Motor Speedway hosted its first race in 1909, even though the event didn’t bring it the fame it deserved.
The track’s surface was suitable for motorcycling but not for car racing. With dirt, rocks, and oil flying from all sides, drivers couldn’t get a good pace, and the race was too dangerous for participants and spectators to keep up.
But that didn’t stop Fisher, who decided to repair the surface with bricks. To strengthen the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, five Indiana manufacturers supplied 3.5 million bricks, each weighing 4.5 kilograms, and hand-laid them, earning the track its second name – The Brickyard.
So, the racing returned to Indianapolis, and it was so fast that drivers could reach a stunning 180km/h.

No less remarkable was the inaugural Indianapolis 500 in 1911. Among forty cars, Ray Harroun won the race and founded the rear-view mirror in car racing. All the other drivers had a mechanic in their vehicle, but Harroun decided to save weight and go faster by driving solo, so he installed a rear-view mirror to see what was happening behind him.
Although the American sport of open-wheel car racing traces its roots to 1905, the first IndyCar race under the American Automobile Association (AAA), the United States Auto Club (USAC), and Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART) took place only on 12 June 1909 in Portland. At the wheel of a Cadillac, Howard Covey won the 3-lap race against five other cars.
However, the term ‘Indy Car‘ has stuck since the Indianapolis 500, although it describes the cars that competed in the USAC open-wheel championship.
Along with the 24 Hours of Le Mans and Formula One Monte Carlo, the Indy 500 completes the Triple Crown of Motorsports racing, which only Graham Hill has yet to achieve.

The Global Racing Revolution
Overall, the 20th century was the golden age of motorsports. It was prestigious. Each country founded its automobile club, while the desire to build the fastest and most reliable car was in the origins of the new manufacturers.
In 1902, the brothers Franz, Karl, and Heinrich Gräf presented the first Austrian-made car, the Gräf & Stift, later known as the MAN.
The same year, Sylvain de Jong founded Minerva, which produced the Belgian-made car and was also used for racing.
František Ringhoffer founded the Czech Republic’s manufacturing company Praga in 1907, whose early racing car models were built under license from Isotta Fraschini, who in his turn presented their racing car in 1905.
Wishing to build the best racing car, forced Fiat racing drivers Vincenzo Lancia and Claudio Fogolin to found Lancia & C. Fabbrica Automobili in 1906 and reveal their first Tipo 51 car or 12 HP(Alfa) in 1908.
The first-ever Japanese-made gasoline engine car was made by Komanosuke Uchiyama in cooperation with Tokyo Motor Vehicles Ltd. in 1907.
In 1909, industrial designer Ettore Bugatti founded Bugatti, which the Type 35 Grand Prix became one of the most successful racing cars of its time.
Italian engineers Nicola Romeo and Ugo Stella founded the Anonima Lombarda Fabbrica Automobili, or Alfa Romeo, in 1910, and their first car – 24 HP participated in the 1911 Targa Florio race.
Meanwhile, after being hired by the Autocar Company to develop a front-wheel-drive racing car, Swiss-American racing driver Louis Chevrolet met Buick’s owner William C. Durant, and four years later, along with his brother Arthur and William Little, they founded the Chevrolet Motor Car Company in 1911.
Being passionate drivers, Lionel Martin and his friend Robert Bamford founded Aston Martin in 1913, naming the company in honor of the Aston Hill Climb, on which Martin and Bamford both had crossed in the annual competition from London to Gloucester, organized by the British Motor Cycling Club (MCC). Coal Scuttle – the first Aston Martin car saw the world in 1915.
However, the following World Wars significantly evolved motorsport racing.
The Impact of World War I and II on Motorsport
Although the changes brought about by the war were primarily related to car production, the effects touched every aspect of racing, destroying some dimensions while rebuilding others.
Establishing New Technologies Suitable For Future Motorsports
For example, World War I efforts spurred innovations in engine design, transmission, and suspension that were later applied to racing cars.
Thus, in military times, it was a crucial need to produce more engines, and that forced Cadillac automobile (1902) founder Henry Martyn Leland to leave the manufactury and launch the Lincoln Motor Company in 1917, in which he tested the Liberty L-12 (V-12 engine), that gave birth to American muscle cars.
Designed for aircraft, the V-12 was the lightest and most powerful engine, which made it ideal for building fast race cars. Thus, in April 1926, John Parry-Thomas broke the land speed record with a Liberty V-12-powered car at 273.6 km/h.
The independent suspension system developed for aircraft landing gear was adapted for racing cars, while solid rubber tires used on military vehicles to improve durability and reduce punctures became the basis for racing tires.
The need for efficient aircraft design led to innovations in aerodynamics. Therefore, manufacturers started to design racing cars using lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys. At just over 1,500 pounds, the 1914 Mercedes Grand Prix car was the lightest car ever built.
The exterior of the racing cars also changed. Elements used in airplane wings to reduce drag, such as the airfoil shape, were adapted for race car bodies, such as the Mercedes-Benz W25 in 1934.

The Following Innovations
The wartime emphasis on standardized parts for military vehicles led to similar practices in race car production, facilitating easier repairs and, therefore, the growth of motorsports.
The disc brakes in military vehicles led to their introduction in racing cars, significantly improving braking performance. Thus, fitted with disc brakes by Dunlop, the Jaguar C-Type became an innovative racing car that won 24 Hours of Le Mans in 1953.
The need for better precise fuel delivery in aircraft engines led to the development of fuel injection systems in racing cars, such as the Mercedes-Benz W196 Formula One car in 1954.

The New Faces in Post-Wars Motorsport
New brands and names entered motorsports with the availability and improvement of new technologies. If World War I forced manufacturers to develop new technologies, World War II changed the existing ones.
Thus, Walter Owen Bentley founded Bentley Motors in 1919, which cars won the 24 Hours of Le Mans five times, while in 1929, they finished 1-2-3.
Founded in 1922 as Swallow Sidecar Company and rebranded as Jaguar in 1945, the brand introduced the Jaguar XK120 in 1948, which became a successful sports car and competed in various racing events, including the Mille Miglia.
In 1927, Japanese industrialist Sakichi Toyoda founded the Toyoda Automatic Loom Works, which, under the guidance of Sakichi’s son Kiichiro Toyoda, would become Japan’s largest automaker, Toyota (1937).
Czech-German automotive engineer Ferdinand Porsche founded Porsche in 1931 with Adolf Rosenberger and Austrian businessman Anton Piëch. After World War II, his son Ferry Porsche switched to racing, which led to the introduction of the Porsche 356 in 1948 and laid the foundation for the brand’s future in motor racing.
As a student at the University of London, English designer Colin Chapman created the Mark1, a modified Austin7, in 1948 for local racing and named his creation Lotus. He launched the Lotus cars in 1952, and after ten years, they won seven Formula 1 Constructors’ titles, six Drivers’ championships, and even the Indianapolis 500 race, while their Lotus 49 (1967) became a dominant force in Formula 1.
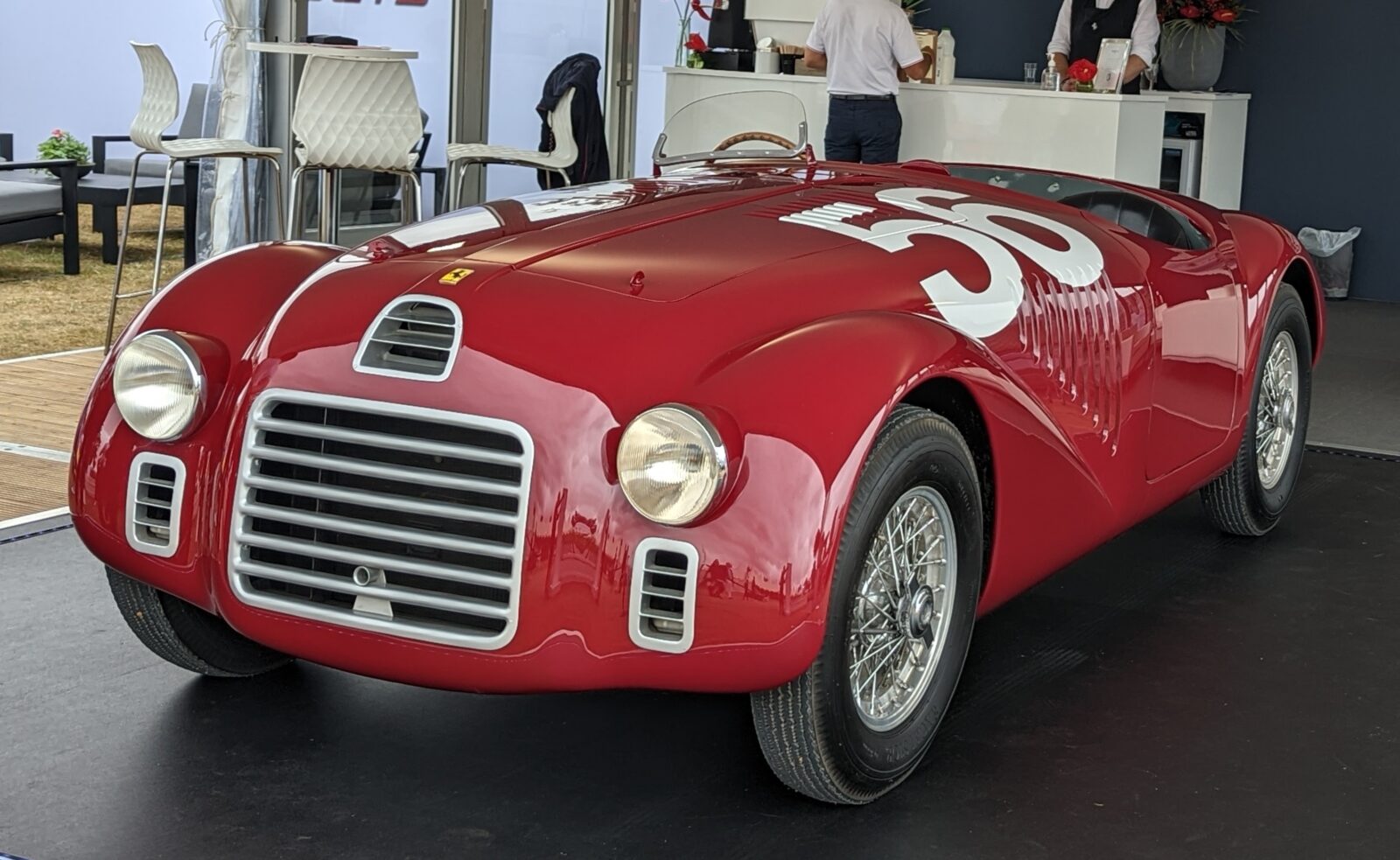

Enzo Ferrari As A Driving Force Of The Motorsport
In 1929, Enzo Ferrari founded Scuderia Ferrari and changed the world of motor racing forever. He quickly brought fame to Alfa Romeo, but by 1938, the automaker decided to re-enter racing under its name – Ferrari. The Ferrari 125 S was the first car to bear the Ferrari name, marking the beginning of Ferrari’s era in motorsport in 1947.
Outside Formula One racing, Ferrari cars had won the World Sportscar Championship, 24 Hours of Le Mans, 24 Hours of Spa, 24 Hours of Daytona, 12 Hours of Sebring, Bathurst 12 Hour, races for Grand Tourer cars, and racing on road courses of the Targa Florio, Carrera Panamericana, and the Mille Miglia.
Enzo Ferrari was a driving force in motorsport worldwide because he originated healthy competition. He supported Italian racing talents like Alberto Ascari, Luigi Villoresi, and Giancarlo Baghetti, but also many others wanted to beat unstoppable racing cars under the Prancing Horse icon.
Alfa Romeo’s team manager, Orazio Satta Puliga, had a long-standing rivalry with Enzo Ferrari and was determined to beat him on the track.
Founded in 1937, Maserati’s owner, Adolfo Orsi, was a close friend and rival of Enzo Ferrari. He wanted to outdo Ferrari on the track and in the market.
Lancia‘s team manager, Vittorio Jano, was a highly respected engineer who challenged Ferrari’s dominance, as did Alfred Neubauer, who had been heading the Mercedes-Benz Grand Prix team from 1926 to 1955.
Just think about how Ferruccio Lamborghini‘s brand had been growing in the background of Enzo Ferrari. Lamborghini decided to create his own sports car and founded Automobili Lamborghini in 1963. Lamborghini Miura in 1966 was the first race car to compete with Ferrari, while Espada aimed to compete with Ferrari’s 365 GTB/4 Daytona.
One of the most iconic rivalries against Enzo Ferrari’s dominance was an attempt by Henry Ford II (grandson of Henry Ford) in the early 1960s. Ford intended to buy Ferrari, but the deal fell through. In response, Ford built a car to beat Ferrari at Le Mans, resulting in the Ford GT40 winning the event in 1966, 1967, 1968, and 1969.
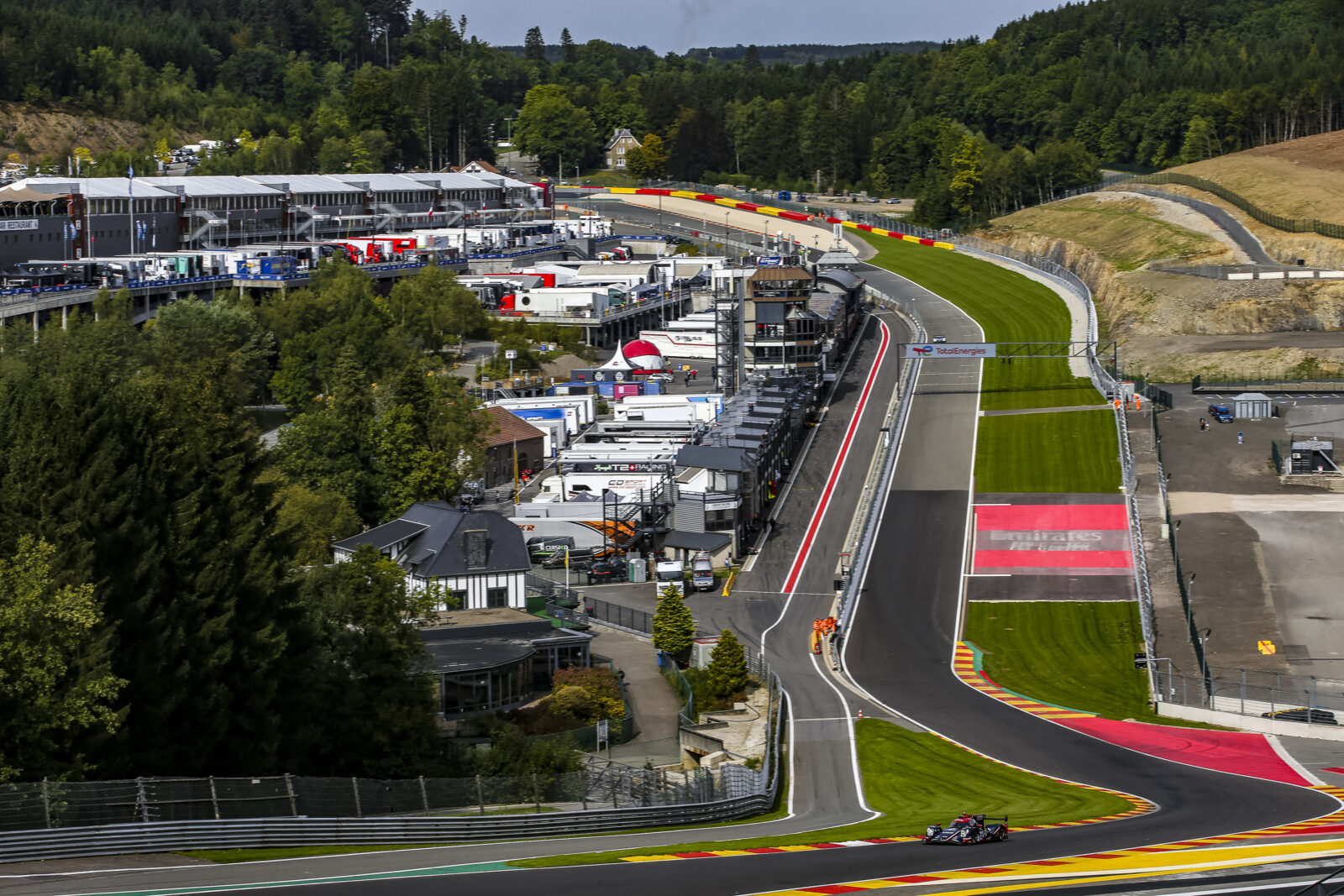

Growth Of Racing Circuits
Many iconic venues were destroyed once forever, such as Brooklands, whose history ended in 1939. However, new technologies needed to be tested as much as possible, so most airplane polygons became race tracks.
Monza Circuit (Italy 1922)
Over 3,500 Italian Automobile Club (ACI) workers had been building Monza Circuit – still the fastest race track in Formula 1. Monza kicked off the 1922 Italian Grand Prix and got its second name – The Template of Speed.
Circuit de Monaco (Monaco 1929)
Under the patronage of the President of the Automobile Club de Monaco, Antony Noghès, the Monaco circuit immediately took on the glamour of the inaugural race in 1929, won by William Grover-Williams at the wheel of the Bugatti.
Formula 1 debuted on the Monaco circuit as the World Drivers’ Championship in 1950.
Circuit of Spa-Francorchamps (Belgium 1922)
The Circuit of Spa-Francorchamps opened in 1921, but the inaugural race was canceled when only one driver entered. Therefore, the first car race was held here in 1922, and 1924 saw the first running of the now famous 24 Hours of Spa, while the first Formula 1 Belgian Grand Prix kicked off in 1925.
Among the others, however, it has preserved most of its original spirit and is still one of the most dangerous, which is why it is rebuilt almost every year as the cars have become faster.
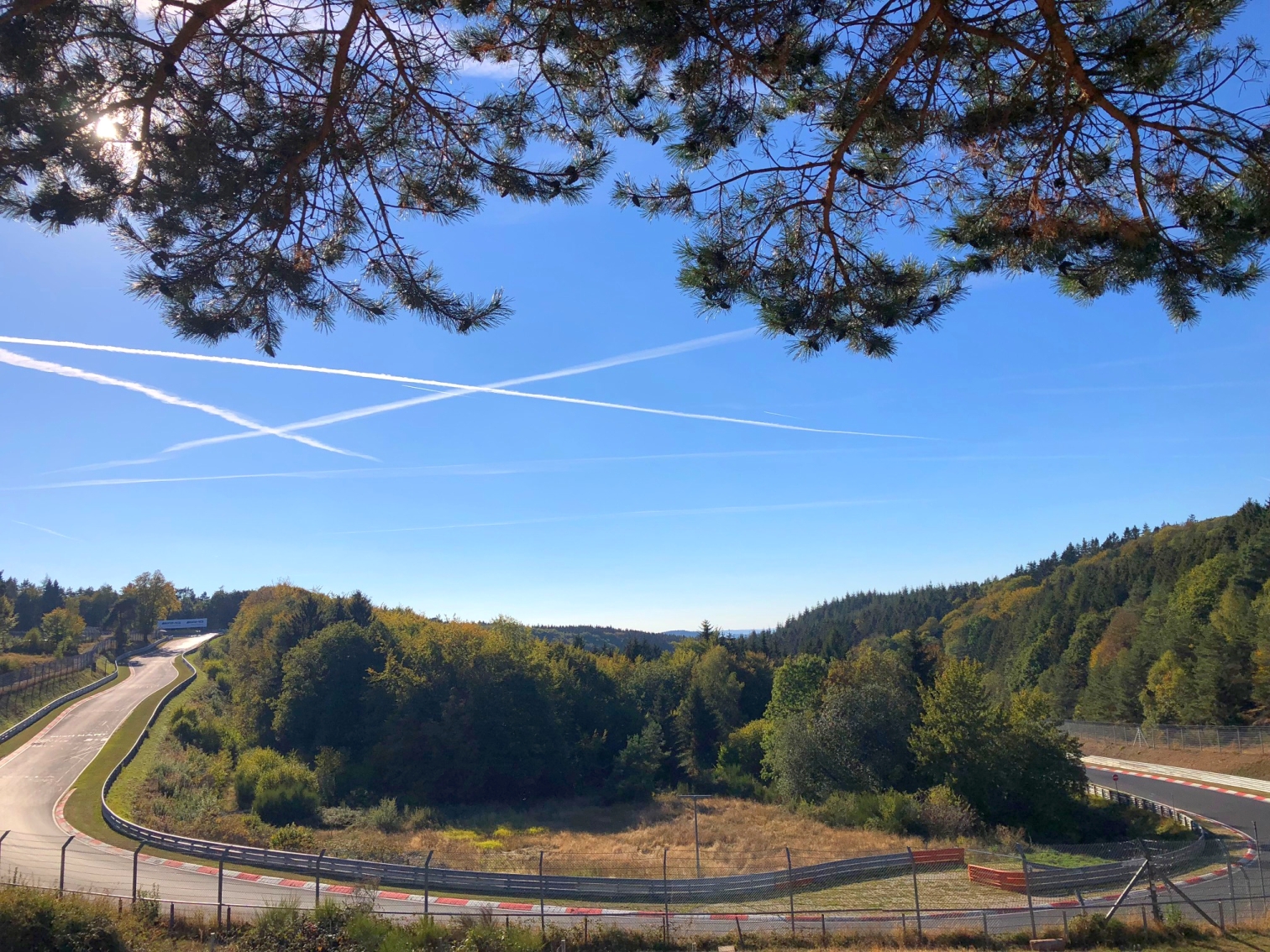

Nürburgring Nordschleife (Germany 1927)
The Nordschleife is part of the Nürburgring, but at this point, it started the story of the circuit in 1927.
The original Nürburgring configuration (Entire Course) consisted of four loops, covering nearly 30 km, whereas the Nordschleife (North Loop) with the 22-kilometer Nordschleife was the first built section.
The track was designed to provide the maximum testing of sports cars for manufacturers to evaluate the performance and durability of their vehicles under various conditions. With its challenging layout surrounded by dense forests, the track contains more than 300 meters of elevation change from the lowest to the highest point, making it the most dangerous circuit.
With supporting of the German automobile club (ADAC), Nürburgring Nordschleife has become the main field for motorsport events, including the 24 Hours of Nürburgring.
Racing in extreme conditions, at the long, fast, and unforgiving layout through its blind corners and narrow roads in the 1967 German Grand Prix, Jackie Stewart labeled the Nürburgring as The Green Hell, which stuck as the track’s second name.
Bernd Rosemeyer
Throughout its long history, Nurburgring has revealed to legendary drivers the world. Bernd Rosemeyer was one of them.
Having started racing motorcycles, Rosemeyer joined the Auto Union racing team. When Ferdinand Porsche designed mid-engine Silver Arrows for the team, only Hans Stuck, Tazio Nuvolari, and Bernd Rosemeyer truly mastered the 500 hp (370 kW) cars.
In only his second-ever Grand Prix at the Nürburgring, Rosemeyer took the lead from the great Rudolf Caracciola and was almost in sight of the finish line when he missed a gear and lost leadership. However, he won three consecutive races at the Nürburgring, one famously in thick fog.
Also, Rosemeyer was a skilled mechanic. He helped Dr. Porsche develop new cars, making them quicker and easier to drive. So, in Rosemeyer’s honor, Audi built a concept car with styling strongly resembling the former Silver Arrows Grand Prix racers, namely their 16-cylinder car Rosemeyer.
Silverstone Circuit (UK 1948)
Originally a wartime airfield, Silverstone was empty for two years before the Royal Automobile Club (RAF) found the circuit’s layout as a perfect field for racing and held the British Grand Prix in 1948. However, the Formula 1 Championship history started with Silverstone in 1950.
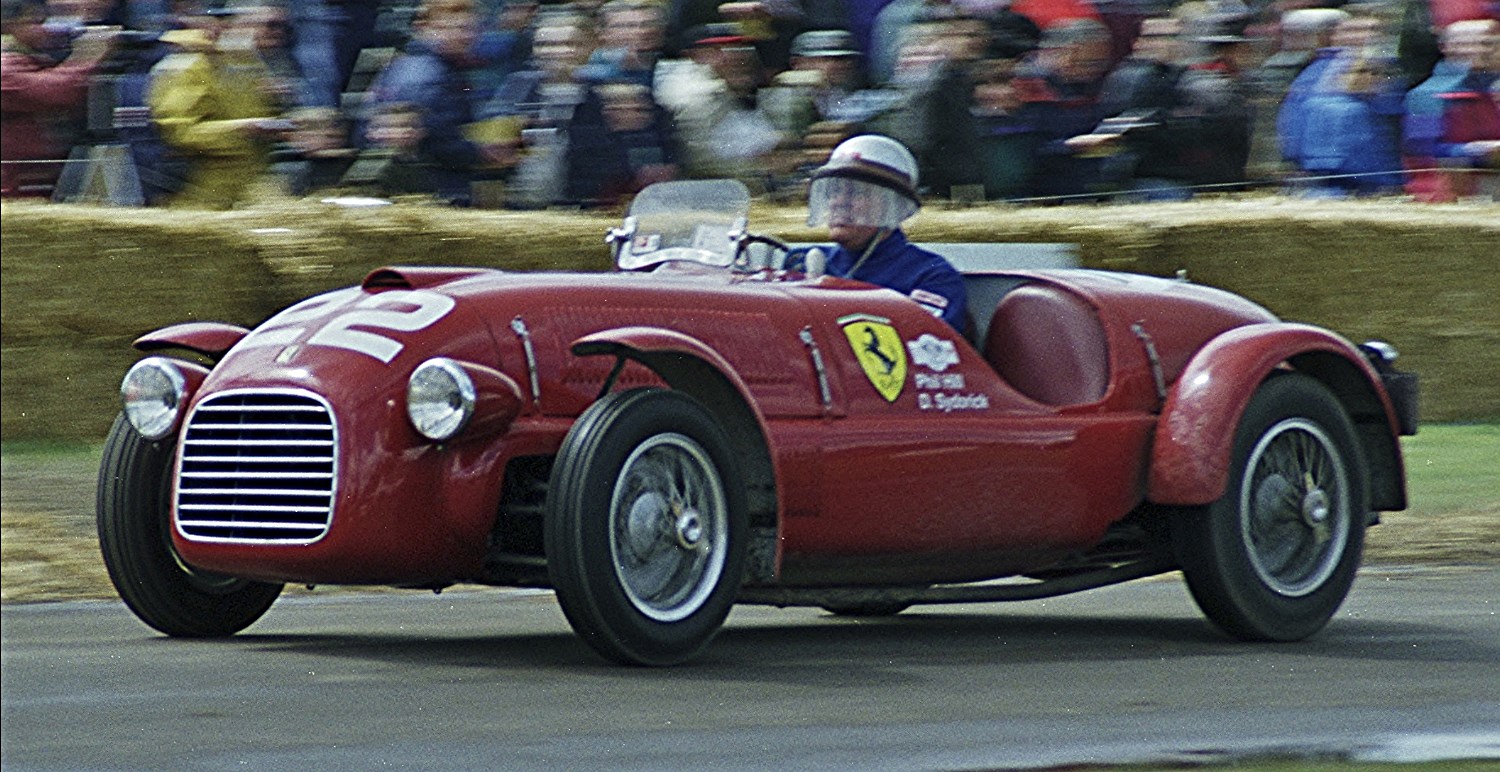

Goodwood Circuit (UK 1948)
Motorsport enthusiast Frederick Gordon-Lennox, 9th Duke of Richmond, built the Goodwood circuit in his home county. It was the perimeter of RAF Westhampnett airfield and well suited for the first race in 1948, organized by the British Automobile Racing Club. The circuit featured a mix of fast straights and challenging nine corners and is approximately 3.862 km long.
However, Goodwood became famous for its Glover Trophy non-championship Formula One race and its races, such as the Goodwood Nine Hours races, running in 1952, 1953, and 1955, and the Tourist Trophy, held between 1958 and 1964.
Goodwood had seen many famous drivers, such as Mike Hawthorn, Graham Hill, Stirling Moss, Roger Penske, and Jim Clark.
Frederick Gordon-Lennox was the longest serving vice-president of the Royal Automobile Club, while Goodwood saw its last race in 1966. The circuit closed its doors because the owners couldn’t agree to modify the track to reduce the speeds of modern cars, although it has hosted the Goodwood Festival of Speed since 1993.
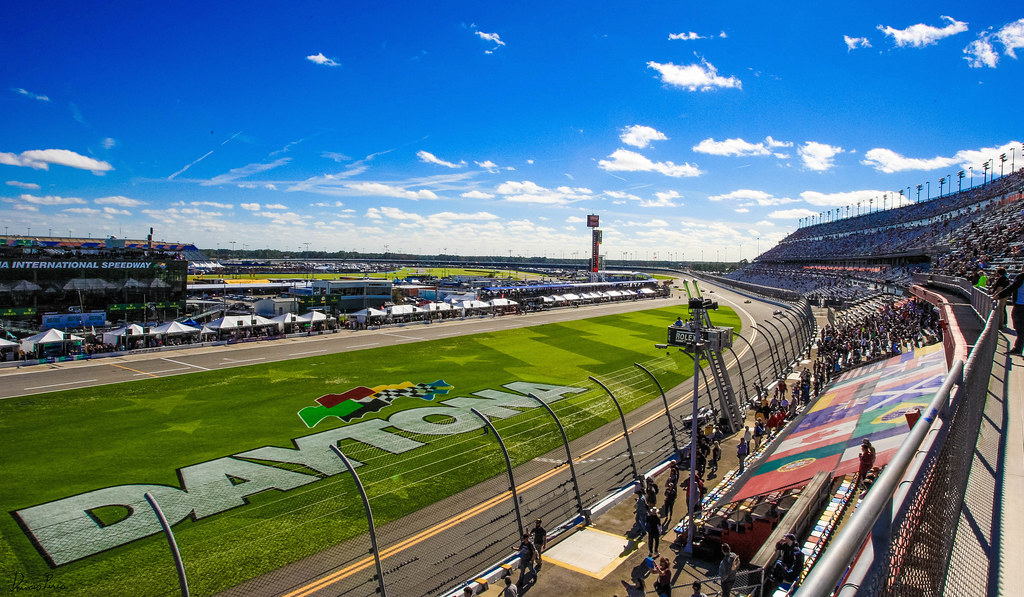

Daytona International Speedway (USA 1959)
Since the National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing (NASCAR) was founded in 1950, the opening of the Daytona International Speedway was just a matter of time.
When NASCAR founder Bill France Sr. (William France Sr.) met with Daytona Beach road course engineer Charles Moneypenny, he already had a vision. France wanted the track to have the highest banking to allow drivers to reach the highest speeds while giving fans a better view of the race.
The ‘World Center of Racing’ or the Daytona International Speedway was completed and hosted the inaugural Daytona 500 race on February 22, 1959.
The track is also famous for the 24 Hours of Daytona, a 24-hour sports car endurance race that was first time held in 1962.
The Appearance Of New Motor Sports Disciplines
As you see, such fast development in the post-war area required new disciplines to figure out the best racing cars. And that is where the legendary races came from.
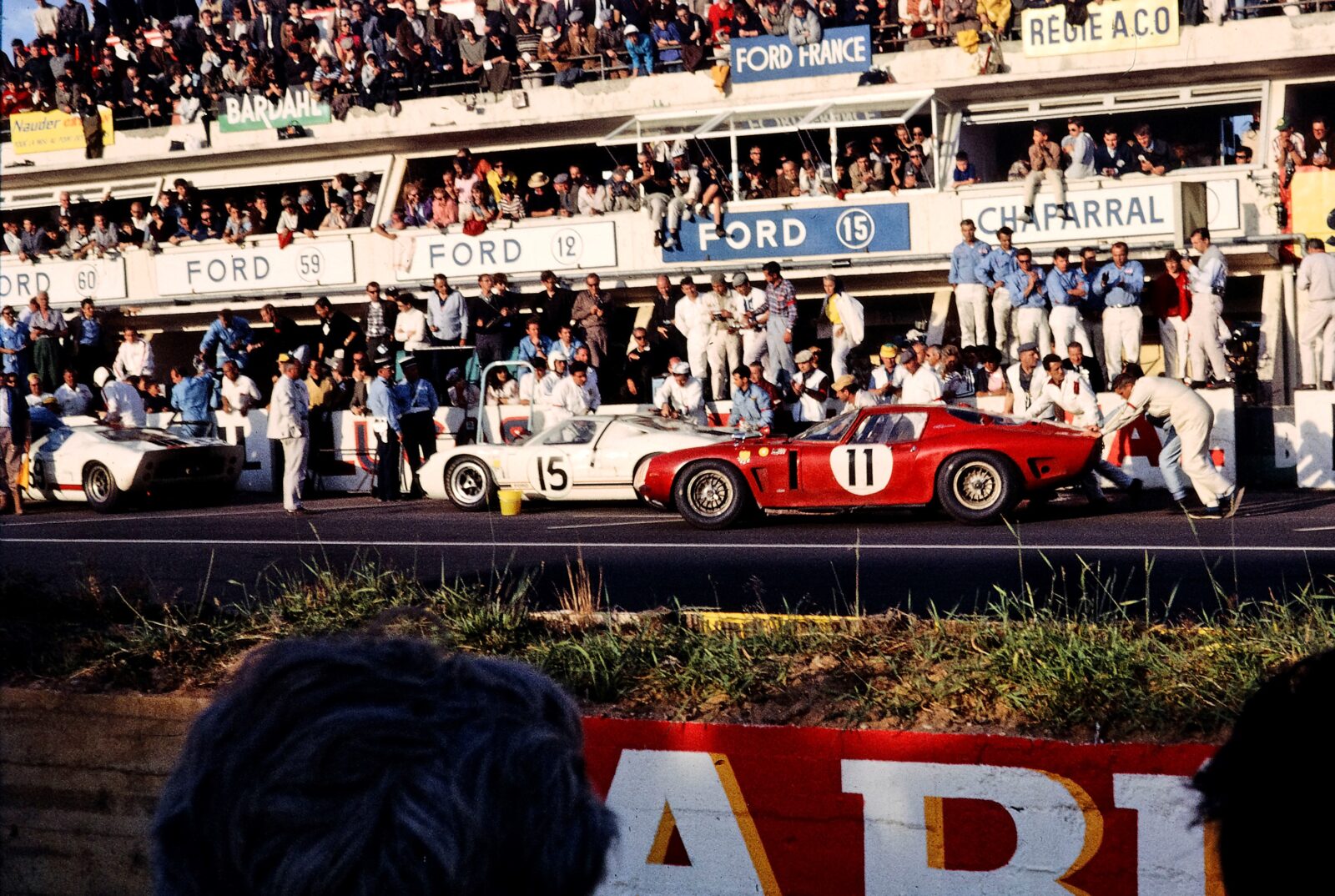

24 Hours of Le Mans (1923 France)
French racing driver Charles Faroux and industrialist Emile launched the first 24 Hours of Le Mans at the Circuit de la Sarthe in Le Mans on May 26-27, 1923, to test the endurance of cars and drivers over a long period, even though the first race was a modest success.
Driving a Chenard & Walcker Type U3 15CV with an average speed of 93 km/h, André Lagache and René Léonard won the race against 32 cars.
Attracting top drivers and manufacturers across Europe, the 24 Hours of Le Mans became a premier event where racers set the top speed records. In 1988, Roger Dorchy reached an astonishing 405 km/h in a WM Peugeot P88.
The event has evolved and completed multiple classes, including the top-tier Hypercar class. So, since 1923, the 24 Hours of Le Mans has been the oldest active endurance race and the most prestigious race in the world.
Inspired by the 24 Hours of Le Mans, businessman Don Panoz created a prominent sports car racing series in North America called the American Le Mans Series (ALMS), which ran from 1999 to 2013.
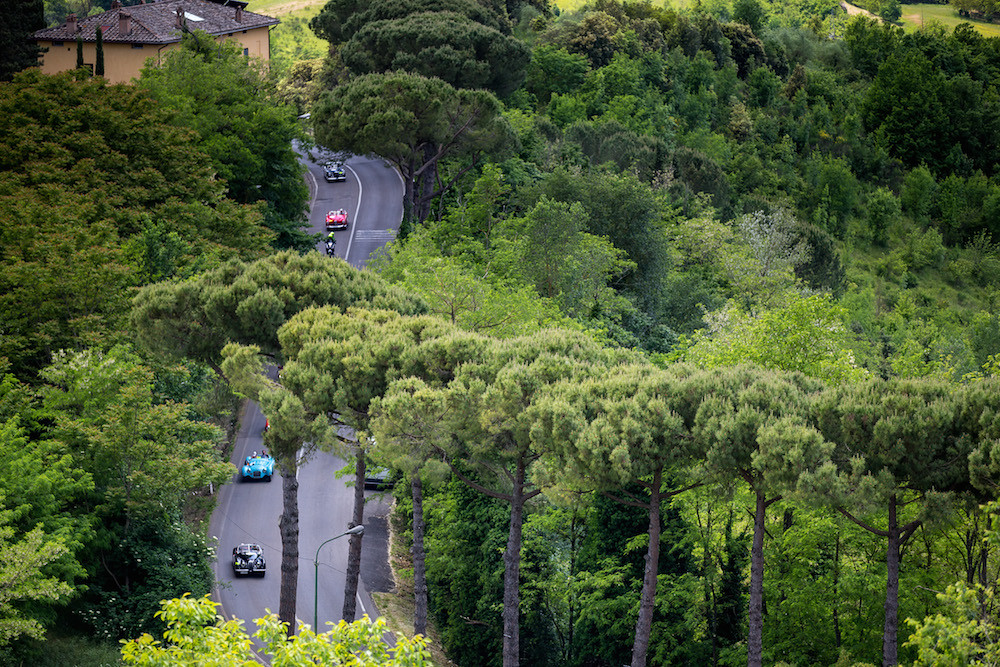

Mille Miglia (Italy 1927)
After World War I, Italian manufacturers, such as Alfa Romeo, Fiat, and Lancia, began producing high-performance vehicles.
To promote Italian cars and showcase the country’s scenic roads, the Automobile Club of Brescia (ACB) and the Automobile Club of Italy (ACI) organized a Thousand Miles or the Mille Miglia race in 1927.
With covering a distance of 1,609 km through the Italian countryside, the inaugural event started and finished in Brescia.
The 1930s was the golden age of the Mille Miglia, as the event attracted the best drivers and manufacturers from all over Europe, including Alfa Romeo, Ferrari, and Mercedes-Benz.
After the war, the Mille Miglia resumed in 1947, attracting new names such as Porsche and Jaguar.
But the history of the Mille Miglia ended in 1957, when a Ferrari 335 S driven by Alfonso de Portago crashed into a crowd of spectators, killing nine people, including the crew. The incident led to a ban on open road racing in Italy, and the Coppa della Sila race replaced Mille Miglia.
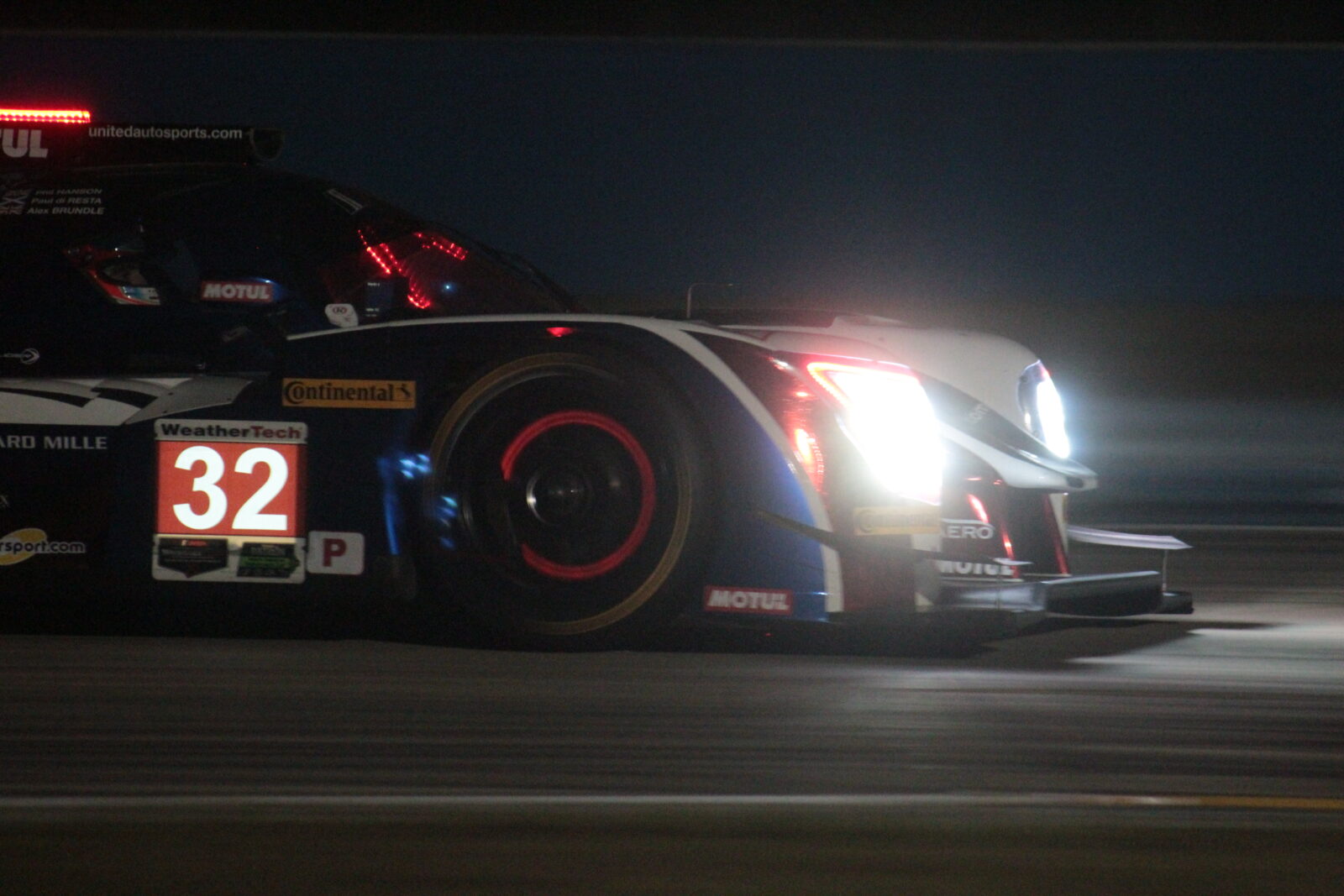

12 Hours of Sebring (United States 1950)
Like most race tracks, Sebring International Raceway was originally an airfield. With the old runways, the track’s layout still reflects its airfield heritage, making it the perfect place to test the limits of the cars.
The first race under the European Grand Prix label in 1950 was only 6 hours long, but the inaugural 12 Hours of Sebring took place on 15th March 1952, mirroring the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
However, the 12 Hours of Sebring was one of the first major endurance races in the United States and was a battleground for Ferrari, Audi, Porsche, BMW, and Ford. Sebring also provided a platform for drivers to hone their skills, helping to develop top racing talent.
After legendary Sebring winners Juan Manuel Fangio, Stirling Moss, and Dan Gurney, Tom Kristensen is still the record holder with six wins in the endurance races at Sebring!
Along with the 24 Hours of Le Mans and 24 Hours of Daytona, the 12 Hours of Sebring is one of the three legs of the Triple Crown of endurance racing.
Since 2014, the event has become the second round of the WeatherTech SportsCar Championship.

The Creation And Origins Of Formula One (Great Britain 1950)
The origin of Formula One Championship or Formula 1 (F1), is difficult to understand because of the confusion of terms.
Formula 1 started in 1950, although the championship had already existed and bore the names of the World Manufacturers’ Championship (1925-1930) and the European Drivers’ Championship (1931-1939) before finally becoming official in 1947 and starting in Great Britain in 1950.
That time, competing for Alfa Romeo, Giuseppe Farina won the first Drivers’ World Championship, but in following years, Farina’s teammate Juan Manuel Fangio won the championship in 1951, 1954, 1955, 1956, and 1957.
Since 1984, every Formula One race has counted towards the World Championship, and every World Championship race has been run according to Formula One regulations. Although the ‘Formula One race’ and ‘World Championship race’ terms are synonymous, they are not interchangeable.
So, Formula 1 started a new era of car racing sport, claiming its number one status year by year, while the high competition in the championship forced manufacturers to design the ideal vehicle.
Thus, in 1961, Bugatti arrived with a significant technological advance when Jack Brabham demonstrated the superiority of a mid-engine car at the wheel. All followed the innovation, and the Ferguson P99 was the last front-engined car to compete in a World Championship.
The following season, the Lotus innovated with an aluminum sheet monocoque chassis, surpassing the traditional space-frame design, and all the participants adapted to the new design. In addition, Lotus discovered Ground Effect Aerodynamics in late 1970.
In turn, Renault pioneered turbocharged engines in 1977, which led to the FIA limiting fuel and banning turbocharged engines by 1989 due to safety concerns.
Sponsorship was introduced in 1968, and Bernie Ecclestone transformed Formula One into a multi-billion dollar enterprise by consolidating commercial rights and negotiating as a collective entity rather than individually in 1970. So, the creation of the Fédération Internationale du Sport Automobile (FISA) in 1979 led to a contentious relationship with the Formula One Constructors’ Association (FOCA) and the Concorde Agreement in 1981.
After high-profile accidents, including the deaths of Ayrton Senna and Roland Ratzenberger in 1994, Formula One underwent new safety improvements, including speed limits and new rules.
The Splitting Into Different Formulas
So Formula 1 has tiered classes: Formula Two (F2) and Formula Three (F3), which provide a structured path for drivers to advance to Formula One (F1).
The ban on 3.0L supercharged led to the introduction of Formula A (for larger cars) and Formula B (later F2) for smaller, less powerful vehicles.
Formula 3’s roots go back to Formula Junior in 1959 – a training formula for young drivers using production-based engines of around 1.0 liters.
Over the years, F2 evolved through various engine regulations and formats, including a 1.5 L era from 1957 to 1960 and a 2.0 L era from 1972 to 1984, before being replaced by Formula 3000, but revived by the FIA from 2009–2012 in the form of the FIA Formula Two Championship.
F2 and F3 have been stepping stones for drivers wanting to reach F1, but F2 is often the penultimate step before F1.
Formula Renault.
As for Formula Renault, in the 1970s, the French manufacturer was involved in single-seater racing by sponsoring the Formula Renault series, which was a more affordable and accessible alternative to Formula 3.
The series has evolved through various iterations, including Formula Renault 1.6, Formula Renault 2.0, and the more recent Formula Renault Eurocup.
Today, Formula Renault is a popular junior open-wheel racing series that has produced many successful drivers, including Sebastian Vettel and Fernando Alonso.

NASCAR (United States 1950)
Despite the existing popularity of open-wheel cars, such as IndyCars and Grand Prix cars, World War II led to the growth of bootlegging in the southern United States, marking the beginning of American stock car racing and the formation of the Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) in 1944, the National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing (NASCAR) in 1948, The National Hot Rod Association (NHRA) in 1951 and formation the new era of cars – Grand Touring (GT).
Thus, talented mechanic, passionate driver, and creative entrepreneur William Henry Getty France, more known as William ‘Bill’ France Sr. or Big Bill, was not just to establish the rules and regulations for stock car racing but also promoted this sport.
It started when he moved to Daytona Beach in 1935 and entered the Daytona race event in 1936. Despite finishing fifth, he came up with a new vision for motorsport, as he minded people would enjoy watching stock cars race, while the drivers deserve more transparent rules, including the payments for the races.
Bill France Sr. took over management of the track in 1938 and increased his influence over the drivers and promoters such as ‘King of the Road’ Erwin ‘Cannonball’ Baker, culminating in the formation of NASCAR in 1948.
He later built the Talladega Superspeedway, which opened in 1969, and the International Motorsports Hall of Fame.
Today, NASCAR is one of the most popular forms of motorsports in the United States, and despite it having evolved significantly with advanced technology and safety features, the core principles of NASCAR remain the same, with a focus on speed, competition, and driver skill.
However, most of the changes would not have been possible without Dan Gurney and Roger Penske.
Dan Gurney
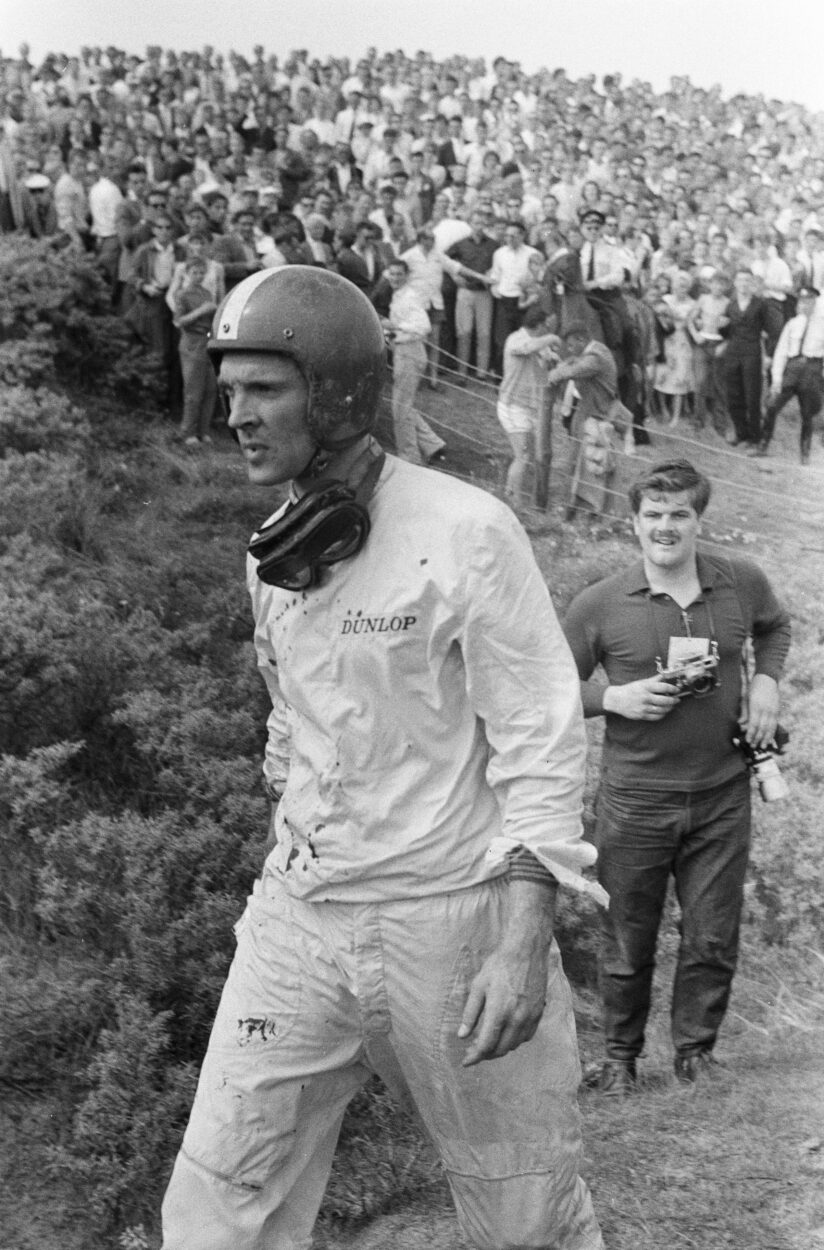

Gurney was a versatile driver. He is the first of three drivers to have won races in sports cars (1958), Formula One (1962), NASCAR (1963), and Indy cars (1967), the other two being Mario Andretti and Juan Pablo Montoya.
With Carol Shelby, Gurney founded All American Racers in 1964, participating in Champ Car races and international Formula One events under the Eagle label.
Gurney launched the champagne shower at the podium in 1967, which became a custom tradition. So, after winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans together with A. J. Foyt, Gurney spontaneously sprayed champagne while celebrating on the podium.
At the 1968 German Grand Prix, Gurney became the first driver ever to wear a full-face helmet in Grand Prix racing.
Gurney was the first to add a simple right-angle extension to the upper trailing edge of the rear wing to increase downforce, more recently known as the Gurney Flap.
Roger Penske
In 1967, Sports Illustrated named Roger Penske the Driver of the Year. Although Penske never raced in the Indianapolis 500, he competed in two Formula One Grand Prixes and won a NASCAR Pacific Coast Late Model race, but he is known for founding one of the most successful teams in IndyCar and NASCAR history, Team Penske.
So, Penske has also been a key figure in promoting motorsport and improving the business aspects, attracting corporate sponsorships and media attention. In 2019, Penske acquired the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.


The Era Of The Grand Touring Cars
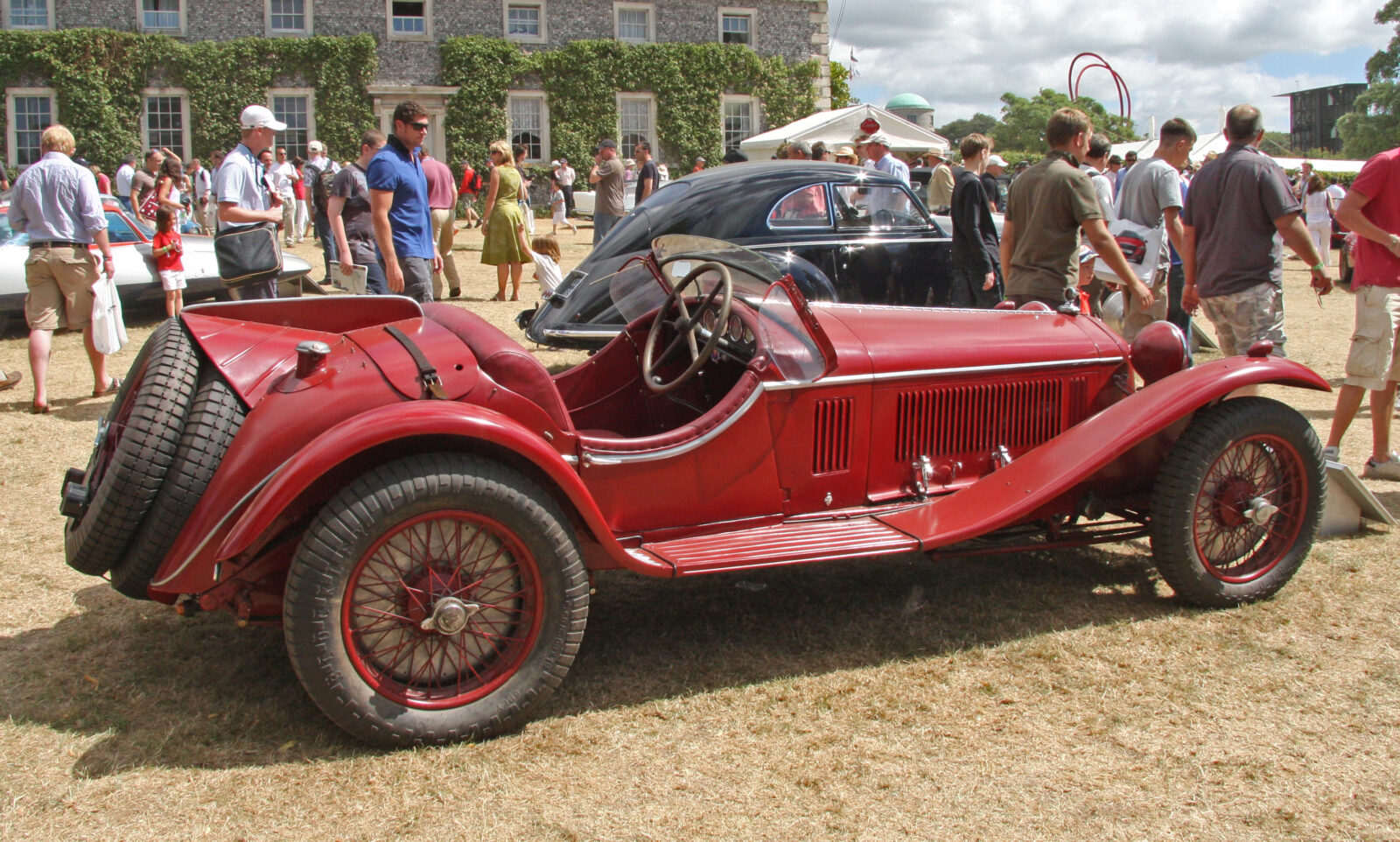
Endurance races such as the Mille Miglia, 24 Hours of Le Mans, and 12 Hours of Sebring played a crucial role in the emergence of fast, agile, but performance-oriented cars – Grand Touring (GT), better known as Grand Turismo.
In the 1920s and 1930s, Alfa Romeo, Bugatti, and Mercedes-Benz began to build high-performance versions of their production cars for racing since speed was no longer a critical factor.
One of the most iconic early GT cars was the Alfa Romeo 8C (1930), which won numerous races, including the 24 Hours of Le Mans in 1931.
However, the concept of GT cars was launched in 1951 when Lancia presented their Aurelia B20 GT so that Vittorio Jano, Enzo Ferrari, and Johnny Lurani started the new era of racing cars.
So, in the 1960s, the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA) created requirements for engine size, weight, and aerodynamics for the GT car class, as we know it today.
The Ferrari 250 GTO (1962), with its lightweight construction, powerful engine, and aerodynamic design, became a dominant force in endurance racing, while based on the legendary Porsche 911, the Porsche 911 GT3 made history in GT racing.
In the United States, the concept of the Grand Tourismo car was different, as manufacturers produced cars suited to their long, straight, smooth roads. The mastermind behind the GT efforts in the United States was Carroll Shelby, who designed the Shelby Cobra and the Ford GT40, which eventually helped Henry Ford II beat Enzo Ferrari at Le Mans.
Thus, the powerful V8 engine and aerodynamic design helped the Ford GT40 to achieve victory at Le Mans in 1966, 1967, 1968, and 1969, marking a significant milestone in American motorsport.
The latest generation Chevrolet Corvette C8.R helped Corvette lead the IMSA SportsCar Championship in the 2020 and 2021 seasons and even win the 2023 World Endurance Championship.
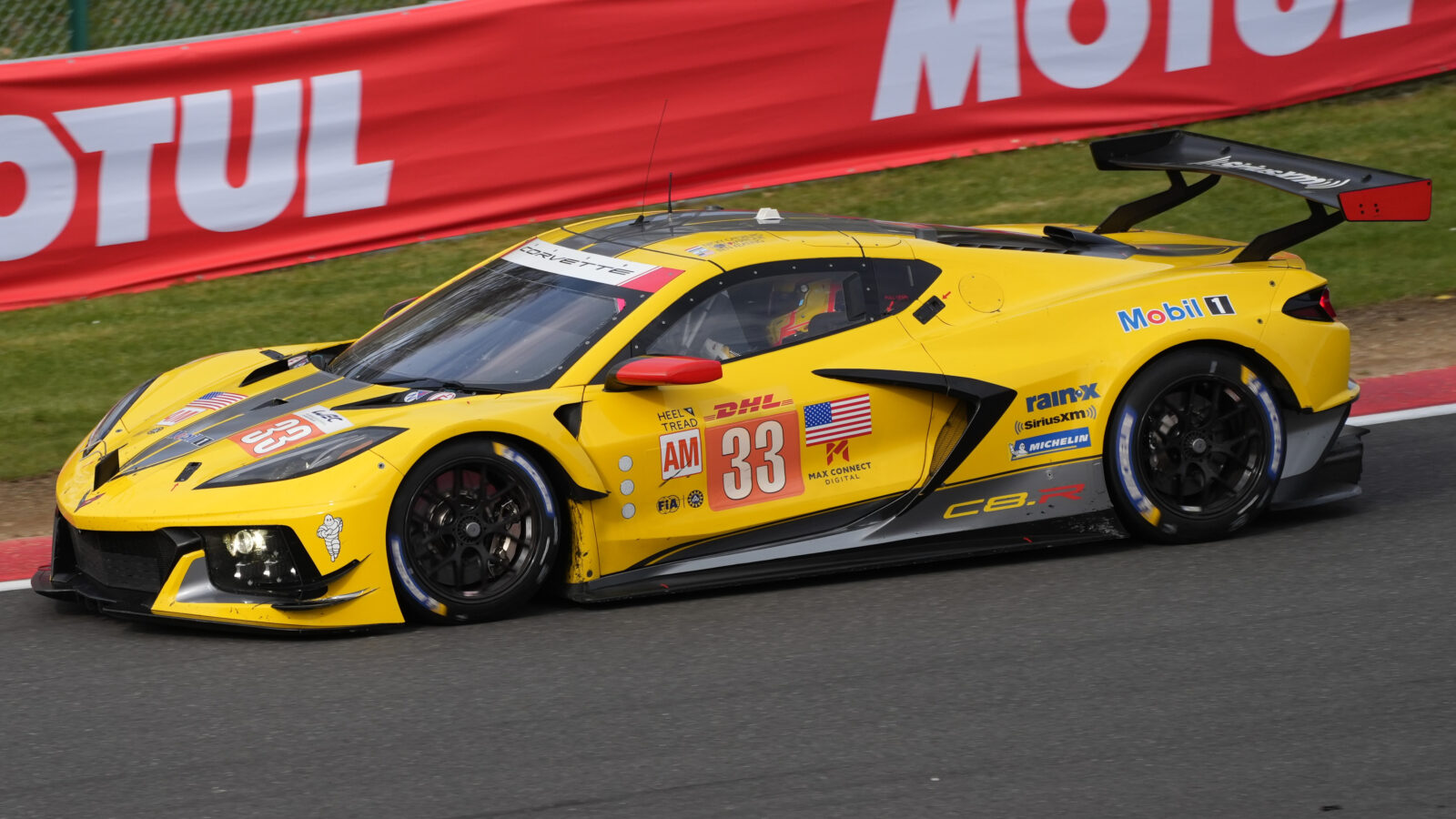

For a better understanding, let’s compare the Porsche 911GT3 (GT) and Porsche 911 Carrera S (non-GT) to illustrate the difference between a GT and a non-GT model.

Porsche 911 GT3 vs Porsche 911 Carrera S
Although the cars look similar at first glance, they are quite different. For example, the Porsche GT3 has a more powerful engine. A naturally aspirated flat-six engine with more horsepower and torque compared to the Carrera S, which has a turbocharged flat-six engine.
With more emphasis on comfort and luxury, the 911 Carrera S is heavier than the Porsche 911 GT3, which has a lightweight construction.
In addition, the GT3 features advanced aerodynamic elements such as larger wings and diffusers for increased downforce and stability at high speeds, while the non-GT features less aggressive aerodynamics for better fuel efficiency and a more comfortable ride.
The Porshe GT3 is also track-oriented, with stiffer suspension and larger brakes for improved handling and braking, while the Carrera’s suspension is softer and more comfortable on public roads.
By focusing on comfort, the Carrera is more luxurious. Its interior features leather seats, premium sound systems, and advanced infotainment systems, while the interior of the Porsche 911 GT3 is stripped down.

Who Were The Female Pioneers In The Motorsport?
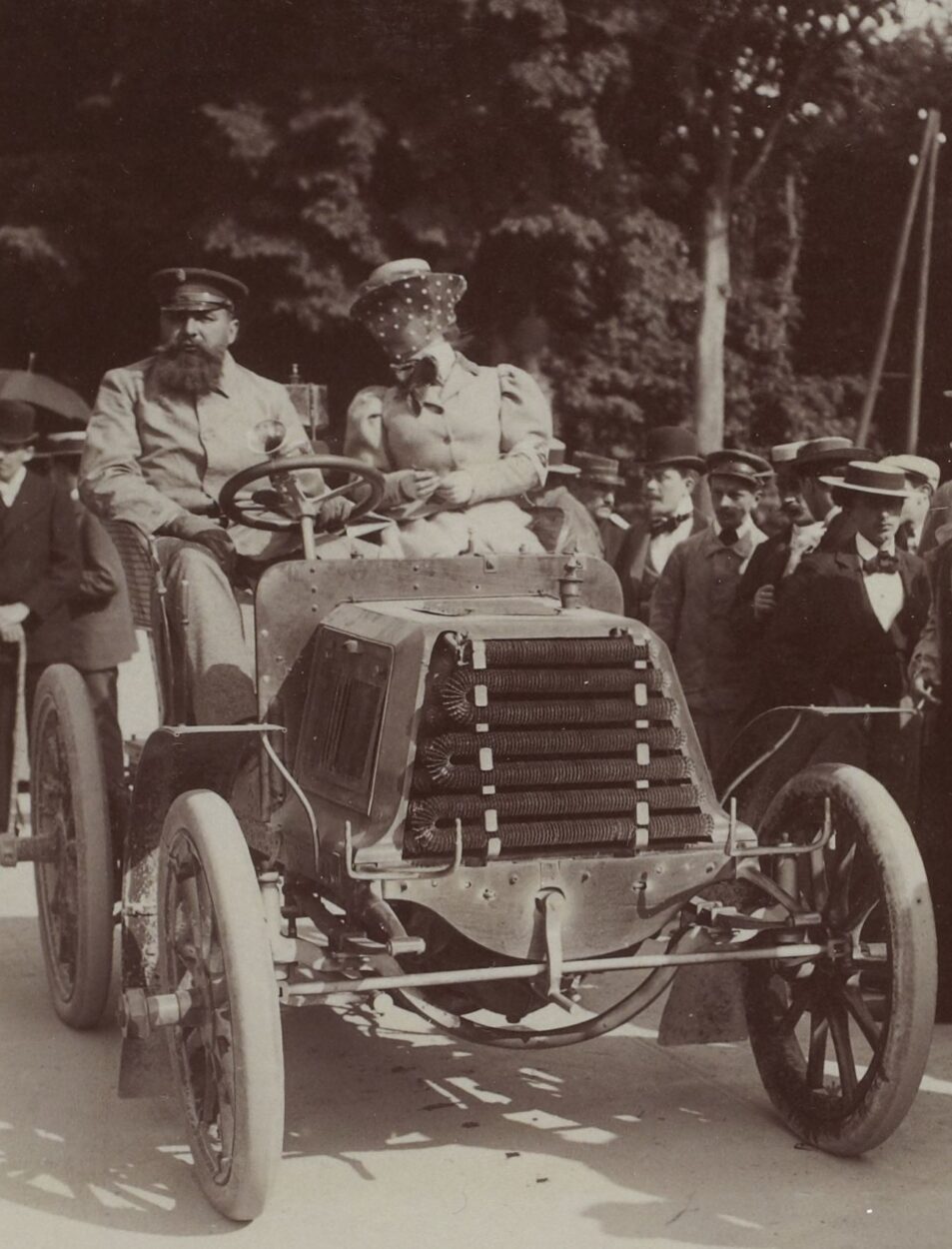
Сontrary to opinions, women had been participating in races too, and the wife of Carl Benz, Bertha, was the first female driver. She took her husband’s car on a famous joyride to demonstrate its capabilities in 1888.
Inspired by the 1900 Gordon Bennett Cup race, Camille du Gast bought a Peugeot and a Panhard et Levassor cars to start the 1901 Paris–Berlin race with the wife of the President of the Automobile Club de France, Hélène van Zuylen. They were the only two women entrants in the event.
One of the great female drivers in Grand Prix motor racing history, Eliska Junkova finished the Targa Florio race in 1926.
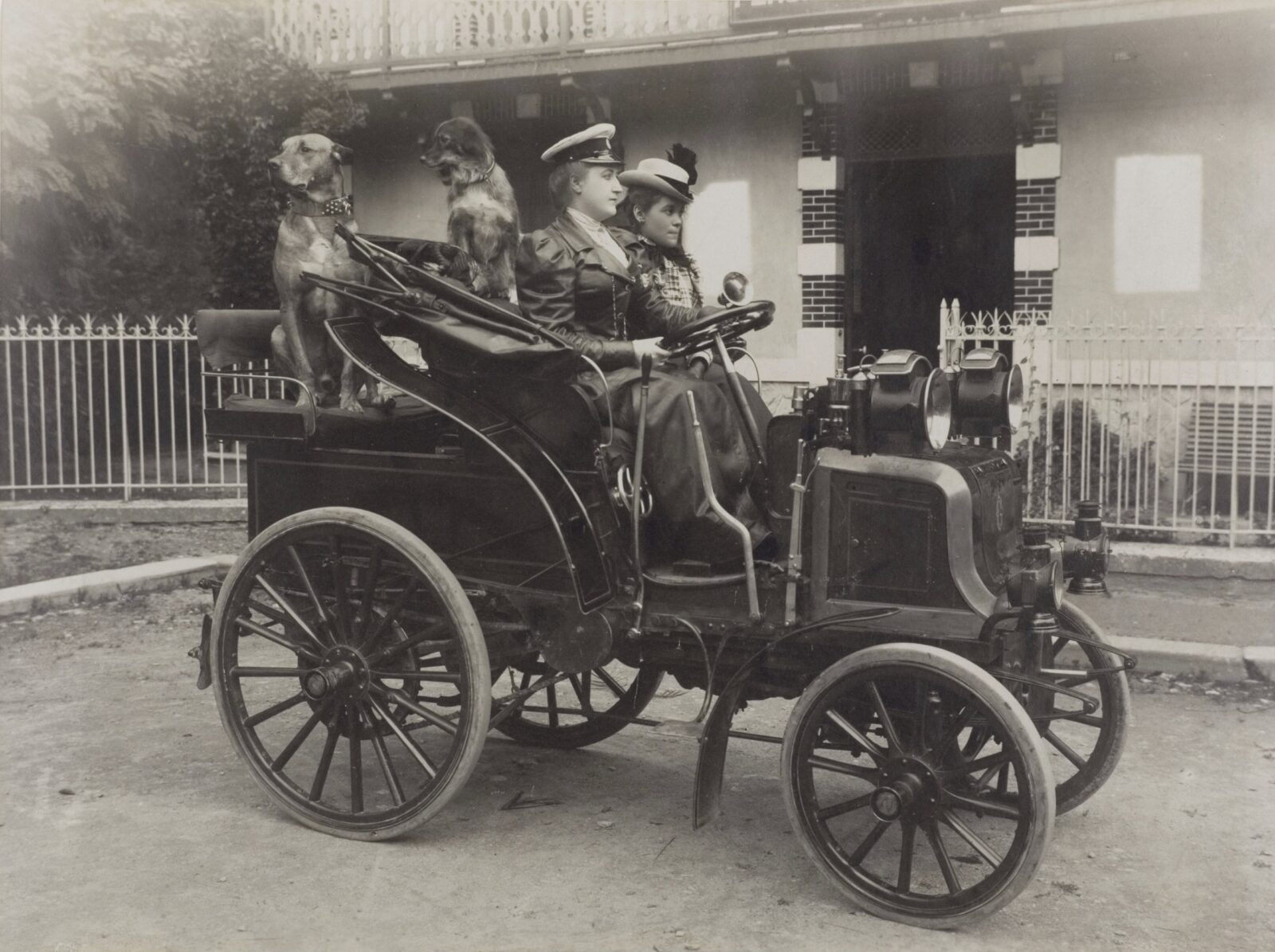

In 1930, Odette Siko became the first female driver to race the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
Driving for Maserati, Maria Teresa de Filippis became the first female Formula 1 racing driver when she debuted at the Syracuse Grand Prix in 1958.
A pioneer for women’s equality in motorsports in the United States, Denise McCluggage earned the respect of her male competitors by winning the Grand Touring category at Sebring in a Ferrari 250 GT in 1961 and a class win at the Monte Carlo Rally in a Ford Falcon in 1964.
Stirling Moss’s younger sister, Pat Moss, was a good rally driver. She finished 6th in her Lotus-tuned Ford Cortina on the 1963 Acropolis Rally.
Lella Lombardi became the second woman to score a championship point in the 1975 Spanish Grand Prix.
In 1977, Janet Guthrie made history as the first woman in the Indy 500 race.

The Shift to Hybrid Technologies (1990s-Present)
We started with the invention of the first car in 1886, but imagine that just over a century later, the whole of motorsport has been gradually transitioning towards hybrid technologies, driven by the need to reduce environmental impact, improve efficiency, and maintain competitiveness.
The move to hybrid technologies offers a more sustainable solution, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing the sport’s carbon footprint.
So in 2014, Formula 1 switched from 2.4-litre naturally aspirated V8 engines to 1.6-litre turbocharged hybrid power units, while the world saw the first Formula E race, which has become a popular platform for sustainable racing, with many top manufacturers competing in the series.
One by one, championships under the FIA’s government have moved to more sustainable technologies, such as the World Rally Championship, which also took to hybrid engines in 2021.
Also, the IMSA WeatherTech SportsCar Championship features a range of hybrid and electric cars, including the Acura NSX GT3 Hybrid and the Porsche 911 RSR Hybrid.
The Le Mans winning cars, the Toyota TS050 Hybrid and Porsche 919 Hybrid, have won multiple Le Mans titles and have been key players in the FIA World Endurance Championship.
The next milestone is set for the 2026 season, and Formula 1 will again be the first to have its cars be fully sustainable, meaning the F1 cars won’t have to burn fossil carbon.

Takeaways
- Being in two different locations, Gottlieb Daimler and Carl Benz simultaneously invented the first-ever cars, even though Benz was the first.
- However, Émile Levassor and René Panhard were the first to create a car for racing – Panhard-Levassor 1205cc.
- With many attempts to hold the car race, Paris-Rouen in 1894 set first, but due to a specific score system, the Paris-Bordeaux-Paris race in 1895 became the official first-ever racing competition.
- However, the Paris-Bordeaux-Paris race brought together influencers from all over the world. The rich, famous, creative, and talented entrepreneurs and engineers were united by a passion for car racing under the Automobile Clubs in different countries.
- It forced new manufacturers founded in the 1900s-1920s in Italy, Great Britain, and the United States while France led the automotive industry.
- Motorsport of that time had risen on two paths, as it was the golden age of endurance races like Targa Florio, Migle Malia, and 24 Hours of Le Mans, and the launching of the Grand Prix.
- Endurance races played a crucial role in the appearance of the Grand Touring or Grand Tourismo – GT cars because the performance became as important as the speed.
- Grand Prix and endurance racing required new venues, and entrepreneurs wanted to build the best circuits, such as Aspendale Racecourse, Brooklands, Indianapolis Motor Speedway, Spa Francorchamps, Monza Circuit, and Nurburgring.
- World Wars I and II revolutionized motorsports with new technologies. Although the V-12 engine, lightweight materials, disc brakes, fuel injection systems, advanced suspensions, and solid rubber tires were developed for aircraft, these were quickly adapted for racing cars.
- The availability of these technologies designed a field for new talented engineers to practice and came with their vision, and Enzo Ferrari was one of them. Ferrari made motorsport the most competitive area because manufacturers like Maserati, Ford, Mercedes, Lamborghini, and many others came to grow to fight back against Prancing Horse.
- Alongside endurance races, it started to grow the American sport – NASCAR, while Formula 1 finally got its official name in the same 1950.
- As soon as the world saw quite fast cars, motorsport had to switch to more sustainable technologies, and the World Championships moved for hybrid power units, and again, Formula 1 was the first.
- Contrary to popular opinion, there were females in the car racing sport who raced alongside men in disciplines such as the 24 Hours of Le Mans, IndyCar, Formula 1, and World Rally Championship.
So the next time you watch any of the motorsport car races, remember its rich history and how people dared innovators. The world’s first race cars may seem simple compared to today’s racing monsters, but they laid the foundation for the thrilling sport we love. And who knows? Maybe the future race cars will look back on today’s vehicles with the same mix of nostalgia and awe.









